
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1186
Question Number 98842 Answers: 2 Comments: 1
Question Number 98833 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 98831 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 98826 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 98823 Answers: 0 Comments: 2

Question Number 98821 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 98818 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
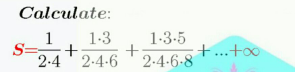
Question Number 98816 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 98815 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$${what}\:{is}\:{heisenberg}\:{uncertainty}\:{principle}? \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Question Number 98808 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
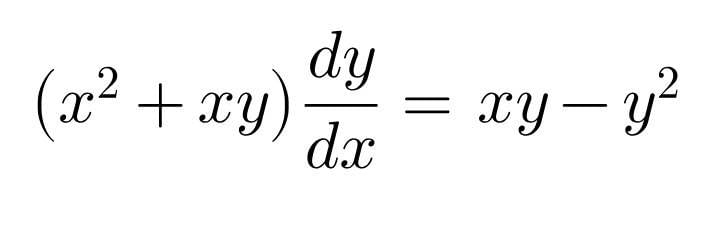
Question Number 98806 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 98788 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 98776 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 98773 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 98770 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
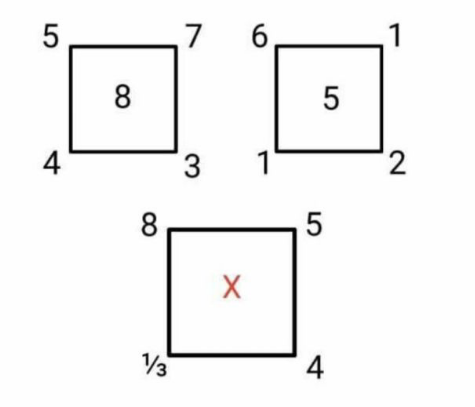
Question Number 98768 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 98761 Answers: 0 Comments: 5
Question Number 98750 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 98744 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 98728 Answers: 0 Comments: 5
Question Number 98723 Answers: 0 Comments: 4
Question Number 98722 Answers: 3 Comments: 0
Question Number 98721 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 98713 Answers: 2 Comments: 1
Question Number 98690 Answers: 1 Comments: 3

Question Number 98687 Answers: 1 Comments: 4

Pg 1181 Pg 1182 Pg 1183 Pg 1184 Pg 1185 Pg 1186 Pg 1187 Pg 1188 Pg 1189 Pg 1190
