
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1180
Question Number 99536 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 99529 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 99516 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 99513 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 99505 Answers: 2 Comments: 2
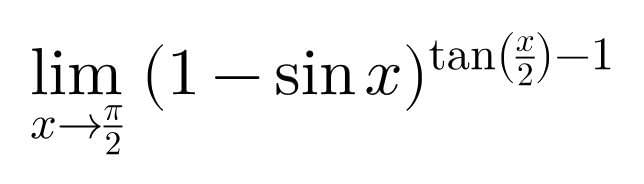
Question Number 99504 Answers: 4 Comments: 0
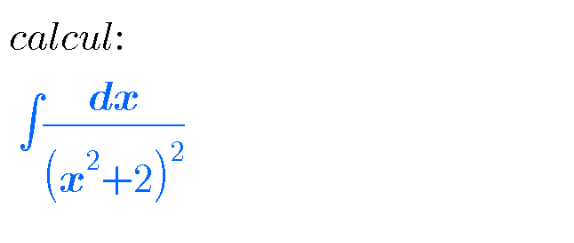
Question Number 99503 Answers: 5 Comments: 0

Question Number 99496 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 99495 Answers: 2 Comments: 2
Question Number 99486 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 99485 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 99464 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 99463 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 99462 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 99465 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 99460 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 99459 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 99458 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 99456 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 99455 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 99494 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 99433 Answers: 2 Comments: 1
$${sin}\mathrm{7}\phi+{cos}\mathrm{2}\phi=−\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${Find},\phi \\ $$
Question Number 99430 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 99429 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 99421 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 99413 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Pg 1175 Pg 1176 Pg 1177 Pg 1178 Pg 1179 Pg 1180 Pg 1181 Pg 1182 Pg 1183 Pg 1184
