
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1139
Question Number 104357 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
$$\left({x}+{y}+\mathrm{1}\right)\:\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}\:=\:\mathrm{1}\: \\ $$
Question Number 104852 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 104851 Answers: 4 Comments: 0
$$\int\:\frac{\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{9}}}{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} }\:{dx}\: \\ $$
Question Number 104850 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 104350 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 104348 Answers: 3 Comments: 0
Question Number 104342 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 104339 Answers: 3 Comments: 1
Question Number 104338 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 104326 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
Question Number 104312 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 104302 Answers: 3 Comments: 2
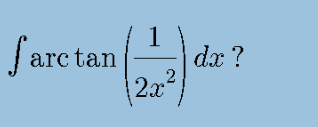
Question Number 104301 Answers: 2 Comments: 2
Question Number 104299 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 104297 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 104296 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 104294 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 104293 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 104286 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 104281 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
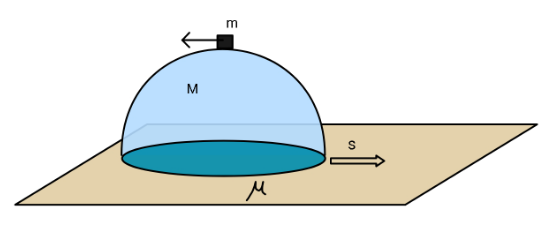
Question Number 104280 Answers: 1 Comments: 5
Question Number 104278 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$${x}−\left(−\left(−{x}+\left(−{x}+{x}\right)\right)\right)=\:? \\ $$
Question Number 104275 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
Question Number 104264 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 104260 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 104253 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Pg 1134 Pg 1135 Pg 1136 Pg 1137 Pg 1138 Pg 1139 Pg 1140 Pg 1141 Pg 1142 Pg 1143
