
AllQuestion and Answers: Page 1004
Question Number 120211 Answers: 3 Comments: 0
Question Number 120209 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 120207 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 120206 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 120204 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 120202 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 120201 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 120196 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 120195 Answers: 3 Comments: 0
Question Number 120194 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
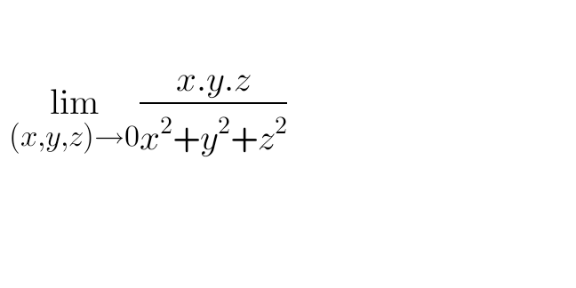
Question Number 120188 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 120186 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 120185 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$${solve}\:{for}\:{x},\:{y}\in{Z} \\ $$$$\sqrt{{x}}+\sqrt{{y}}=\sqrt{\mathrm{2020}} \\ $$
Question Number 120183 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 123960 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 120279 Answers: 0 Comments: 2

Question Number 120277 Answers: 2 Comments: 1
Question Number 120166 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 120160 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 120156 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 120154 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 120152 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 120151 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 120147 Answers: 1 Comments: 1

Question Number 120133 Answers: 0 Comments: 5

Question Number 120132 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Pg 999 Pg 1000 Pg 1001 Pg 1002 Pg 1003 Pg 1004 Pg 1005 Pg 1006 Pg 1007 Pg 1008
