
AlgebraQuestion and Answers: Page 363
Question Number 19403 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 19555 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 19391 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 19351 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
Question Number 19350 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 19349 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
Question Number 19332 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 19405 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 19329 Answers: 0 Comments: 5
Question Number 19313 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 19312 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 19250 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
Question Number 19247 Answers: 1 Comments: 2

Question Number 19245 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 19215 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 19204 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 19198 Answers: 1 Comments: 7
Question Number 19171 Answers: 1 Comments: 1
Question Number 19135 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 19123 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 19121 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 19101 Answers: 0 Comments: 3
Question Number 19095 Answers: 0 Comments: 3

Question Number 19063 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 19073 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
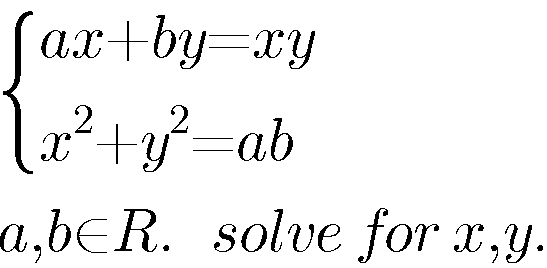
Question Number 18979 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Pg 358 Pg 359 Pg 360 Pg 361 Pg 362 Pg 363 Pg 364 Pg 365 Pg 366 Pg 367
