
AlgebraQuestion and Answers: Page 356
Question Number 23471 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 23357 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 23334 Answers: 1 Comments: 3
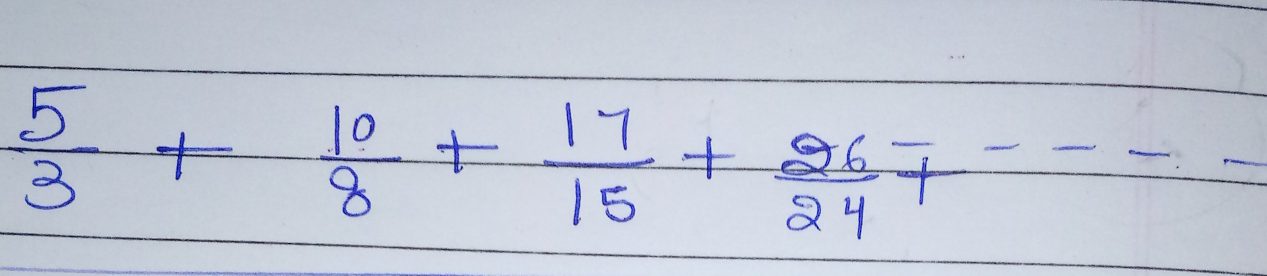
Question Number 23323 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 23250 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 23208 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 23096 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 23000 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 22945 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 22856 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
$$\mathrm{solve}:\:\mathrm{sin}\left({x}\right)=\mathrm{2},\:\:\:{x}\in\mathbb{C} \\ $$
Question Number 22768 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
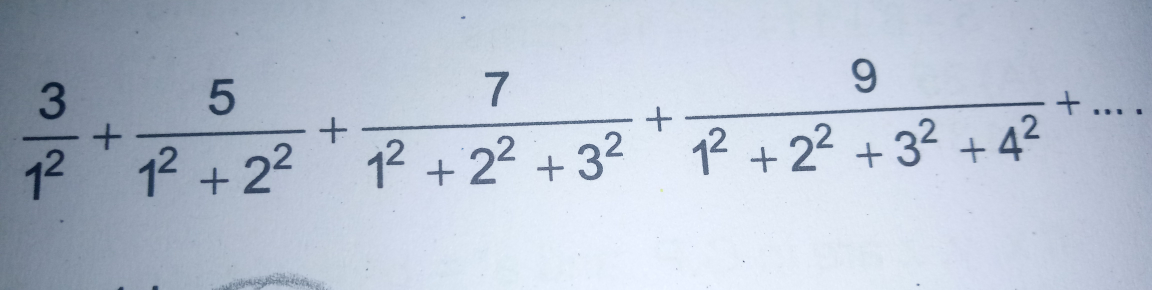
Question Number 22739 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 22701 Answers: 2 Comments: 0

Question Number 22618 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 22640 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 22612 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 22547 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 22517 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 22503 Answers: 1 Comments: 4
Question Number 22491 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 22474 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 22472 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 22468 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 22463 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 29184 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 22423 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Pg 351 Pg 352 Pg 353 Pg 354 Pg 355 Pg 356 Pg 357 Pg 358 Pg 359 Pg 360
