
AlgebraQuestion and Answers: Page 347
Question Number 29885 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
$$\int\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{sin}{x}}{dx}=? \\ $$
Question Number 29837 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 29832 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 29820 Answers: 1 Comments: 3

Question Number 29805 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 29786 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 29777 Answers: 2 Comments: 5
Question Number 29647 Answers: 0 Comments: 1

Question Number 29520 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 29433 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$$\mathrm{4}\left(\mathrm{2x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)=\mathrm{8}^{\mathrm{x}} \\ $$
Question Number 29424 Answers: 0 Comments: 8
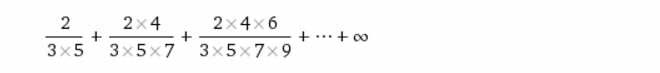
Question Number 29362 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
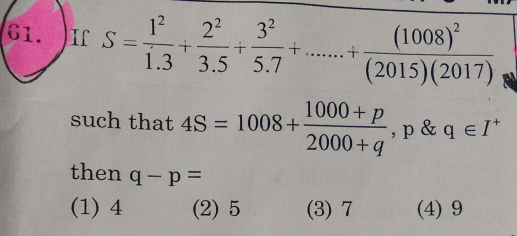
Question Number 29345 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 29264 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 29259 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 29196 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 29167 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 29166 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 29165 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 29164 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 29138 Answers: 0 Comments: 4
Question Number 29123 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
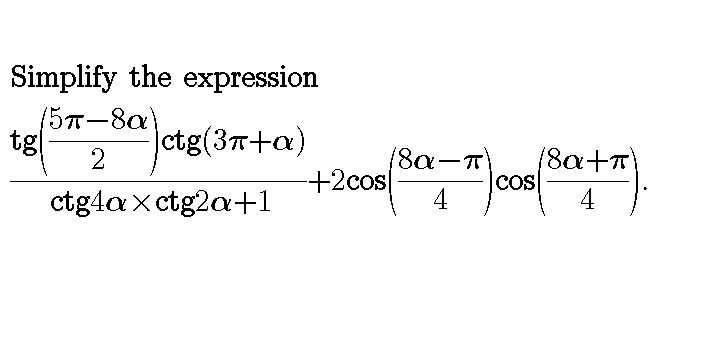
Question Number 29049 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$${Prove}\:{that} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:{e}^{{i}\pi} +\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Question Number 28921 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 28857 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 28856 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Pg 342 Pg 343 Pg 344 Pg 345 Pg 346 Pg 347 Pg 348 Pg 349 Pg 350 Pg 351
