
AlgebraQuestion and Answers: Page 251
Question Number 110879 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
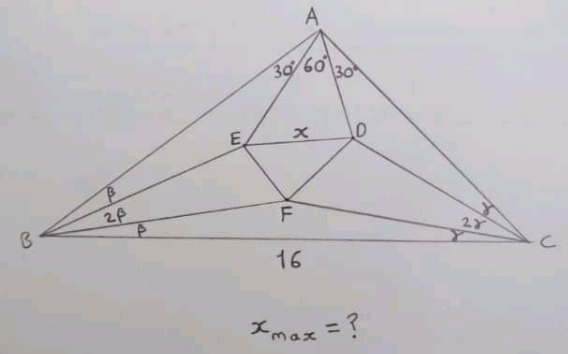
Question Number 110843 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 110837 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 110799 Answers: 0 Comments: 0
Question Number 110845 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 110728 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
$${a}+{b}=\mathrm{9}\:\:,\:\:{ab}=\mathrm{20}\:\:\:\:\:{a}−{b}=? \\ $$
Question Number 110727 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 110706 Answers: 0 Comments: 0

Question Number 110675 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 110620 Answers: 1 Comments: 0

Question Number 110608 Answers: 0 Comments: 1
Question Number 110704 Answers: 3 Comments: 0
Question Number 110596 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
Question Number 110594 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 110593 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 110592 Answers: 3 Comments: 0
Question Number 110673 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
Question Number 110587 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 110586 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 110725 Answers: 2 Comments: 0
$${x}^{{x}^{{x}^{{x}^{...} } } } =\mathrm{2}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{x}=? \\ $$
Question Number 110545 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
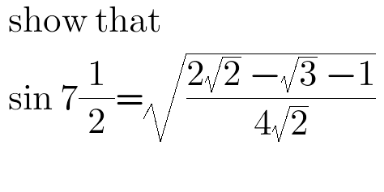
Question Number 110887 Answers: 1 Comments: 2

Question Number 110715 Answers: 1 Comments: 2
Question Number 110490 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 110471 Answers: 1 Comments: 0
Question Number 110463 Answers: 0 Comments: 2
$$\mathrm{Find}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{gcd}\left({n}−\mathrm{1},{n}+\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$
Pg 246 Pg 247 Pg 248 Pg 249 Pg 250 Pg 251 Pg 252 Pg 253 Pg 254 Pg 255
