
Question Number 49186 by afachri last updated on 04/Dec/18

$$\boldsymbol{\mathrm{please}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{help}}... \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\mathrm{There}\:\mathrm{is}\::\: \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{21}\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\mathrm{2}} \:−\:\mathrm{21}\boldsymbol{{p}}\:\boldsymbol{{x}}\:+\:\mathrm{49}\boldsymbol{{p}}\:−\:\mathrm{7}\:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{whose}\:\mathrm{roots}\:\boldsymbol{{u}}\:\mathrm{and}\:\boldsymbol{{v}}.\:\mathrm{If}\:\boldsymbol{{u}}\:\mathrm{and}\:\boldsymbol{{v}}\:\mathrm{are}\:\mathrm{not}\:\in\mathbb{Z}\:,\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{and}\:\boldsymbol{{u}},\boldsymbol{{v}}\:\geqslant\:\mathrm{1}. \\ $$$$\mathrm{find}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{value}\:\mathrm{of}\:\boldsymbol{{u}}\:+\:\boldsymbol{{v}}\:! \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by MJS last updated on 04/Dec/18

$$\mathrm{strange}\:\mathrm{question}...\:\mathrm{there}'\mathrm{s}\:\mathrm{not}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{single}\:\mathrm{solution} \\ $$
Commented by afachri last updated on 04/Dec/18
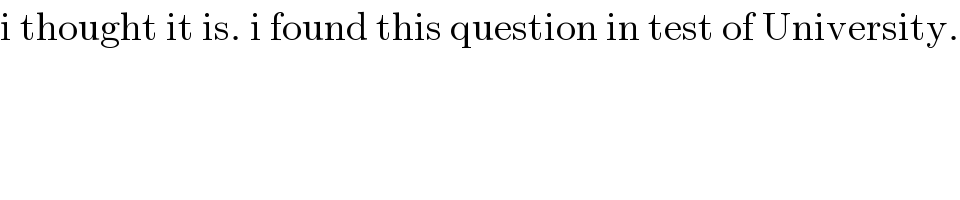
$$\mathrm{i}\:\mathrm{thought}\:\mathrm{it}\:\mathrm{is}.\:\mathrm{i}\:\mathrm{found}\:\mathrm{this}\:\mathrm{question}\:\mathrm{in}\:\mathrm{test}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{University}. \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 04/Dec/18
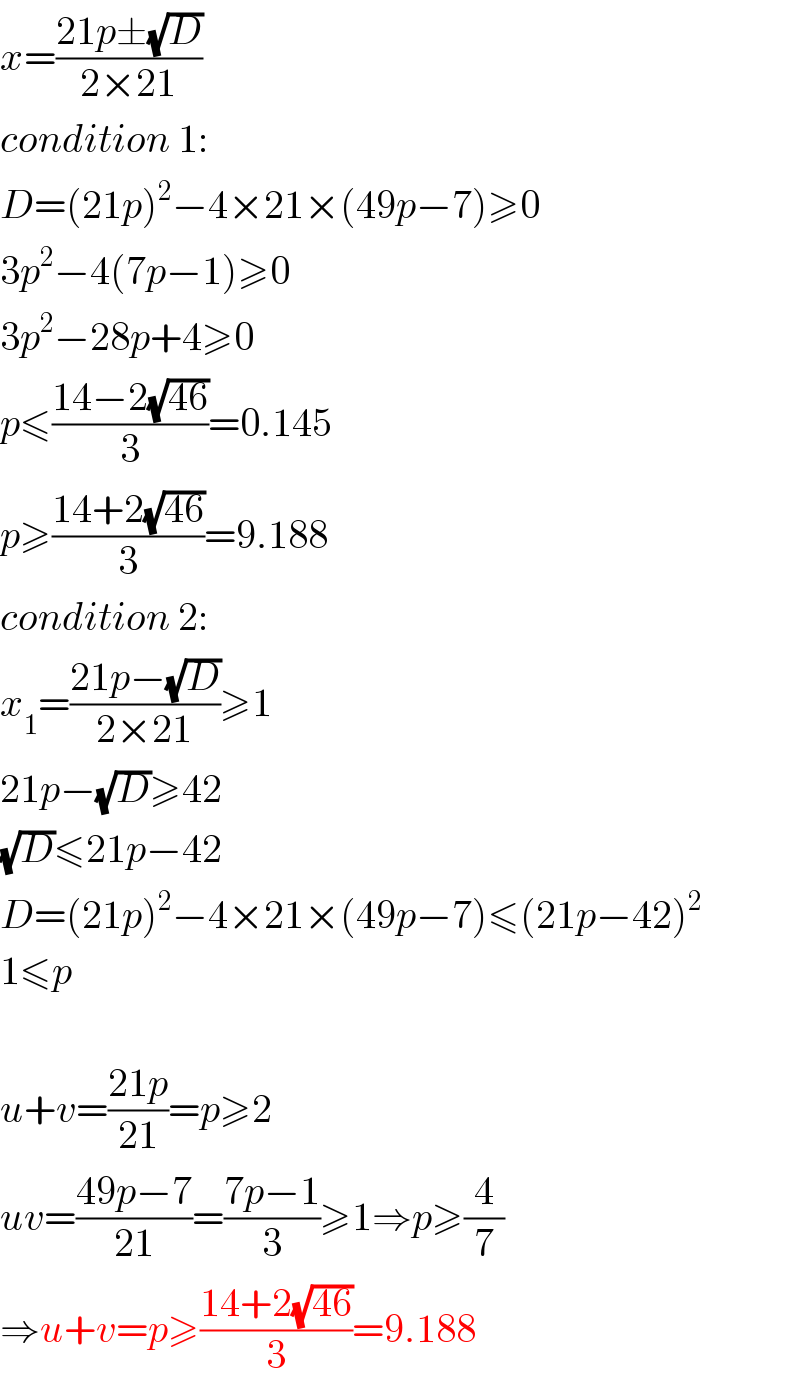
$${x}=\frac{\mathrm{21}{p}\pm\sqrt{{D}}}{\mathrm{2}×\mathrm{21}} \\ $$$${condition}\:\mathrm{1}: \\ $$$${D}=\left(\mathrm{21}{p}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}×\mathrm{21}×\left(\mathrm{49}{p}−\mathrm{7}\right)\geqslant\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{3}{p}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}\left(\mathrm{7}{p}−\mathrm{1}\right)\geqslant\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{3}{p}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{28}{p}+\mathrm{4}\geqslant\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${p}\leqslant\frac{\mathrm{14}−\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{46}}}{\mathrm{3}}=\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{145} \\ $$$${p}\geqslant\frac{\mathrm{14}+\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{46}}}{\mathrm{3}}=\mathrm{9}.\mathrm{188} \\ $$$${condition}\:\mathrm{2}: \\ $$$${x}_{\mathrm{1}} =\frac{\mathrm{21}{p}−\sqrt{{D}}}{\mathrm{2}×\mathrm{21}}\geqslant\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{21}{p}−\sqrt{{D}}\geqslant\mathrm{42} \\ $$$$\sqrt{{D}}\leqslant\mathrm{21}{p}−\mathrm{42} \\ $$$${D}=\left(\mathrm{21}{p}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}×\mathrm{21}×\left(\mathrm{49}{p}−\mathrm{7}\right)\leqslant\left(\mathrm{21}{p}−\mathrm{42}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{1}\leqslant{p} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${u}+{v}=\frac{\mathrm{21}{p}}{\mathrm{21}}={p}\geqslant\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${uv}=\frac{\mathrm{49}{p}−\mathrm{7}}{\mathrm{21}}=\frac{\mathrm{7}{p}−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\geqslant\mathrm{1}\Rightarrow{p}\geqslant\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{7}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{u}+{v}={p}\geqslant\frac{\mathrm{14}+\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{46}}}{\mathrm{3}}=\mathrm{9}.\mathrm{188} \\ $$
Commented by afachri last updated on 04/Dec/18
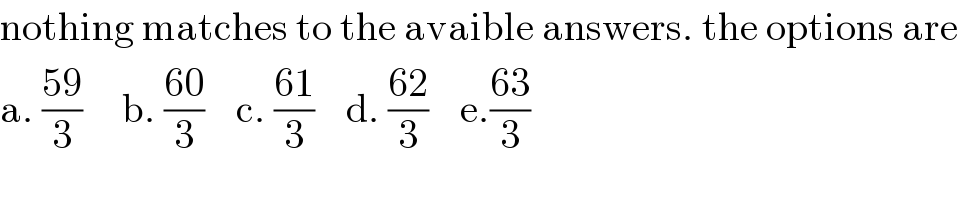
$$\mathrm{nothing}\:\mathrm{matches}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{avaible}\:\mathrm{answers}.\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{options}\:\mathrm{are} \\ $$$$\mathrm{a}.\:\frac{\mathrm{59}}{\mathrm{3}}\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{b}.\:\frac{\mathrm{60}}{\mathrm{3}}\:\:\:\:\mathrm{c}.\:\frac{\mathrm{61}}{\mathrm{3}}\:\:\:\:\mathrm{d}.\:\frac{\mathrm{62}}{\mathrm{3}}\:\:\:\:\mathrm{e}.\frac{\mathrm{63}}{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$
Answered by MJS last updated on 04/Dec/18
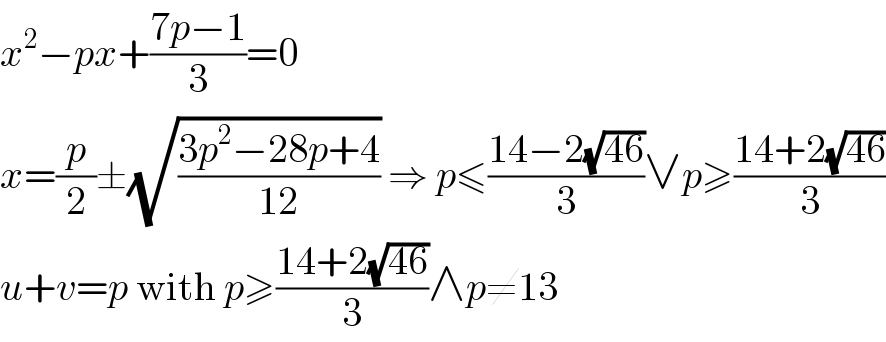
$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} −{px}+\frac{\mathrm{7}{p}−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${x}=\frac{{p}}{\mathrm{2}}\pm\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{3}{p}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{28}{p}+\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{12}}}\:\Rightarrow\:{p}\leqslant\frac{\mathrm{14}−\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{46}}}{\mathrm{3}}\vee{p}\geqslant\frac{\mathrm{14}+\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{46}}}{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$${u}+{v}={p}\:\mathrm{with}\:{p}\geqslant\frac{\mathrm{14}+\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{46}}}{\mathrm{3}}\wedge{p}\neq\mathrm{13} \\ $$
