
Question Number 34367 by rahul 19 last updated on 05/May/18
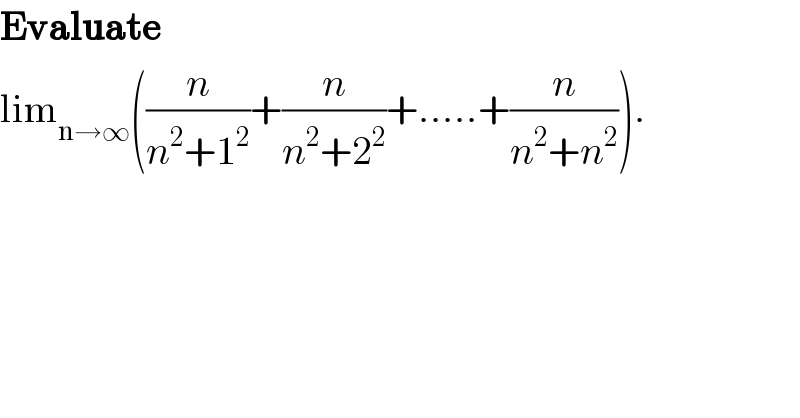
$$\boldsymbol{\mathrm{Evaluate}}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{lim}_{\mathrm{n}\rightarrow\infty} \left(\frac{{n}}{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}^{\mathrm{2}} }+\frac{{n}}{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{2}} }+.....+\frac{{n}}{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} +{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right). \\ $$
Answered by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 05/May/18
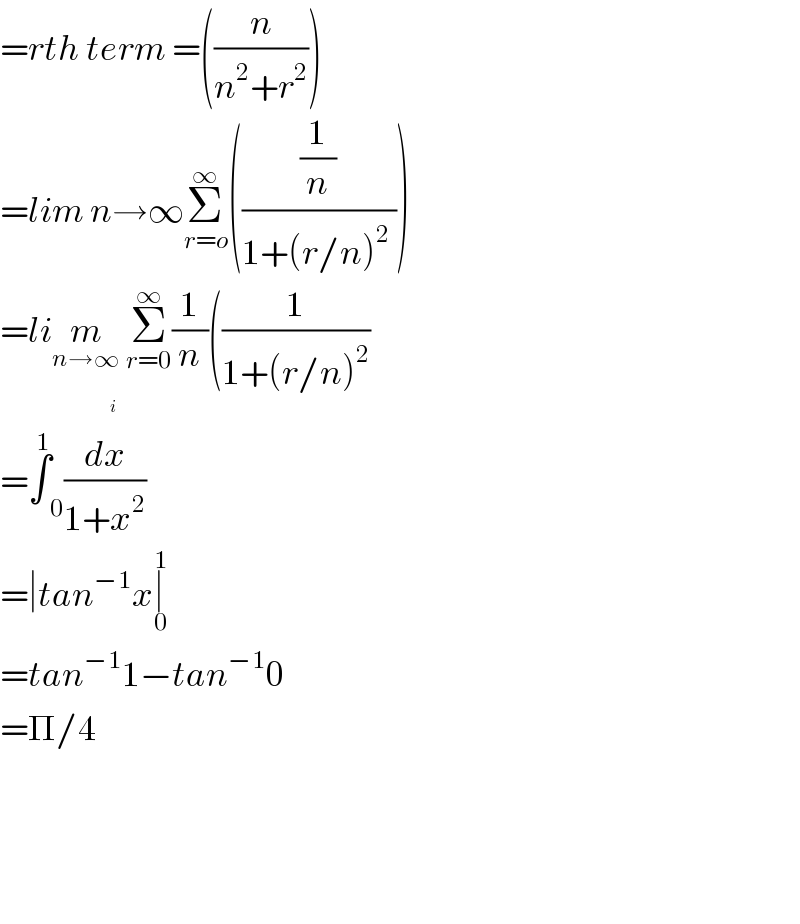
$$={rth}\:{term}\:=\left(\frac{{n}}{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} +{r}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right) \\ $$$$={lim}\:{n}\rightarrow\infty\underset{{r}={o}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\left(\frac{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}}{\mathrm{1}+\left({r}/{n}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \:}\right) \\ $$$$={li}\underset{{n}\rightarrow\infty} {{m}}\:\underset{{r}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+\left({r}/{n}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\right. \\ $$$$=\overset{\mathrm{1}} {\int}\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\:}\frac{{d}\overset{} {{x}}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$=\mid{tan}^{−\mathrm{1}} {x}\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\mathrm{1}} {\mid}} \\ $$$$={tan}^{−\mathrm{1}} \mathrm{1}−{tan}^{−\mathrm{1}} \mathrm{0} \\ $$$$=\Pi/\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by rahul 19 last updated on 05/May/18
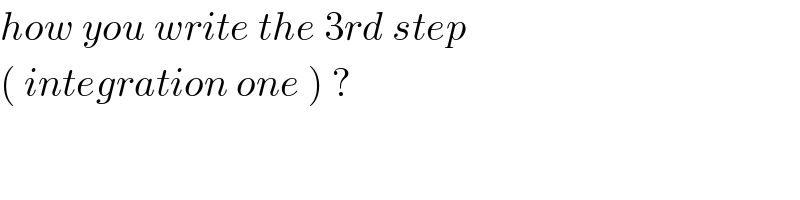
$${how}\:{you}\:{write}\:{the}\:\mathrm{3}{rd}\:{step} \\ $$$$\left(\:{integration}\:{one}\:\right)\:? \\ $$
Commented by math khazana by abdo last updated on 05/May/18

$${its}\:{a}\:{Rieman}\:{sum}\:{sir}\:{Rahul}... \\ $$
Commented by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 05/May/18

Commented by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 05/May/18

Commented by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 05/May/18

Commented by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 05/May/18

Commented by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 05/May/18

Commented by rahul 19 last updated on 05/May/18

$$\mathscr{T}{hank}\:{you}\:{sir}. \\ $$
Commented by abdo mathsup 649 cc last updated on 05/May/18
![let take S_n =[ (1+(1/n^2 ))(1+(2^2 /n^2 ))....(1+(n^2 /n^2 ))]^(1/n) ln(S_n ) =(1/n)ln( Π_(k=1) ^n (1+(k^2 /n^2 ))) =(1/n) Σ_(k=1) ^n ln(1+((k/n))^2 )→∫_0 ^1 ln(1+x^2 )dx ∫_0 ^1 ln(1+x^2 )dx = [x ln(1+x^2 )]_0 ^1 −∫_0 ^1 x ((2x)/(1+x^2 ))dx =ln(2) −2 ∫_0 ^1 ((x^2 +1−1)/(1+x^2 ))dx =ln(2) −2 +2 ∫_0 ^1 (dx/(1+x^2 )) =ln(2) −2 + +2 (π/4) = ln(2) +(π/2) −2 so lim_(n→+∞) S_n = ln(2)+ (π/2) −2 .](Q34412.png)
$${let}\:{take}\:\:{S}_{{n}} =\left[\:\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)....\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)\right]^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}} \\ $$$${ln}\left({S}_{{n}} \right)\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}{ln}\left(\:\prod_{{k}=\mathrm{1}} ^{{n}} \left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{{k}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)\right) \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}\:\sum_{{k}=\mathrm{1}} ^{{n}} \:{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\left(\frac{{k}}{{n}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\rightarrow\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} {ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right){dx} \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\:{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right){dx}\:=\:\left[{x}\:{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:−\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:{x}\:\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx} \\ $$$$={ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\:\:−\mathrm{2}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\:\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx} \\ $$$$={ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\:−\mathrm{2}\:\:+\mathrm{2}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\:\:\:\frac{{dx}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$={ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\:−\mathrm{2}\:+\:+\mathrm{2}\:\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}\:=\:{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\:+\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\:−\mathrm{2}\:{so} \\ $$$${lim}_{{n}\rightarrow+\infty} \:\:{S}_{{n}} \:=\:{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)+\:\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\:−\mathrm{2}\:. \\ $$
