
Question Number 196024 by York12 last updated on 16/Aug/23
![lim_(x→0^+ ) [xΣ_(n=1) ^∞ ((1/n^(x+1) ))]=λ , evalute λ](Q196024.png)
$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}^{+} } {\mathrm{lim}}\left[{x}\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}^{{x}+\mathrm{1}} }\right)\right]=\lambda\:,\:{evalute}\:\lambda \\ $$
Answered by mr W last updated on 16/Aug/23
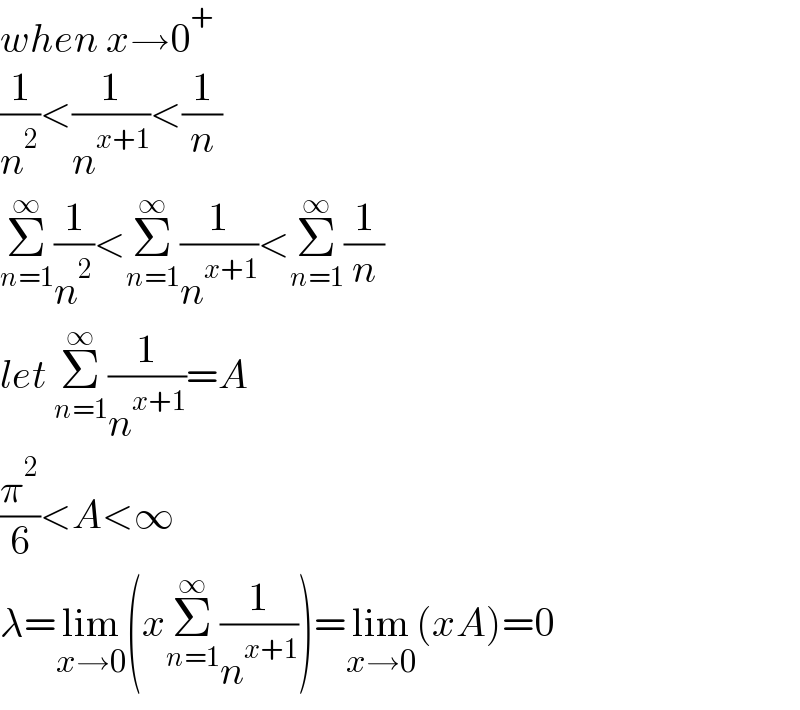
$${when}\:{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}^{+} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }<\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}^{{x}+\mathrm{1}} }<\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}} \\ $$$$\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }<\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}^{{x}+\mathrm{1}} }<\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}} \\ $$$${let}\:\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}^{{x}+\mathrm{1}} }={A} \\ $$$$\frac{\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{6}}<{A}<\infty \\ $$$$\lambda=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\left({x}\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}^{{x}+\mathrm{1}} }\right)=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\left({xA}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Commented by York12 last updated on 17/Aug/23

$${thanks} \\ $$
