
Question Number 194942 by horsebrand11 last updated on 20/Jul/23

$$\:\:\:\:\: \\ $$
Commented by MJS_new last updated on 20/Jul/23

$$−\mathrm{2} \\ $$
Commented by horsebrand11 last updated on 20/Jul/23

$$\:\mathrm{how}\:? \\ $$
Answered by MJS_new last updated on 20/Jul/23

$$\mathrm{2}{x}=\mathrm{2}{y}^{\mathrm{3}} +\left(\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}\right){y} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}{y}=\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +\left(\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}\right){x} \\ $$$${y}={px} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}{x}=\mathrm{2}{p}^{\mathrm{3}} {x}^{\mathrm{3}} +\left(\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}\right){px} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}{px}=\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +\left(\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}\right){x} \\ $$$${x}=\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow\:{y}=\mathrm{0}\:\mathrm{but}\:{x}\neq{y}\:\Rightarrow\:{x}\neq\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}={p}\left(\mathrm{2}{p}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}{p}=\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}} \\ $$$$========== \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} =\frac{\mathrm{2}−\left(\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}\right){p}}{\mathrm{2}{p}^{\mathrm{3}} }=\frac{\mathrm{2}{p}−\left(\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}\right)}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${p}^{\mathrm{4}} −\frac{\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}}{p}^{\mathrm{3}} +\frac{\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}}{p}−\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{know}\:\mathrm{that}\:{x}=\pm{y}\:\Rightarrow\:{p}=\pm\mathrm{1}\:\:\mathrm{are}\:\mathrm{solutions}, \\ $$$$\mathrm{now}\:\mathrm{it}'\mathrm{s}\:\mathrm{easy}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{factorize} \\ $$$$\left({p}−\mathrm{1}\right)\left({p}+\mathrm{1}\right)\left({p}^{\mathrm{2}} −\frac{\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}}+\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{but}\:{x}\neq{y}\wedge{x}+{y}\neq\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${p}^{\mathrm{2}} −\frac{\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}}+\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${p}=\mathrm{e}^{\pm\mathrm{i}\pi/\mathrm{5}} \\ $$$${y}={px}\:\Rightarrow\:\frac{{x}}{{y}}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{p}}\wedge\frac{{y}}{{x}}={p} \\ $$$$\left(\frac{{x}}{{y}}\right)^{\mathrm{2025}} +\left(\frac{{y}}{{x}}\right)^{\mathrm{2025}} =\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{405}\pi\mathrm{i}} +\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{405}\pi\mathrm{i}} =\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{i}\pi} +\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{i}\pi} = \\ $$$$=−\mathrm{2} \\ $$
Commented by horsebrand11 last updated on 20/Jul/23
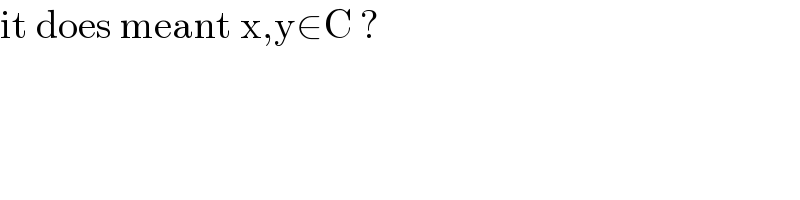
$$\mathrm{it}\:\mathrm{does}\:\mathrm{meant}\:\mathrm{x},\mathrm{y}\in\mathrm{C}\:? \\ $$
Commented by MJS_new last updated on 20/Jul/23

$$\mathrm{yes} \\ $$
Commented by horsebrand11 last updated on 20/Jul/23

$$\mathrm{thanks}\:\mathrm{sir} \\ $$
Commented by MJS_new last updated on 20/Jul/23
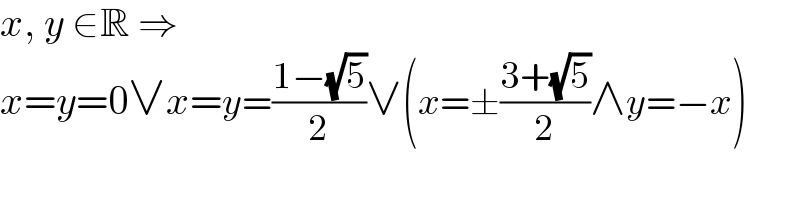
$${x},\:{y}\:\in\mathbb{R}\:\Rightarrow\: \\ $$$${x}={y}=\mathrm{0}\vee{x}={y}=\frac{\mathrm{1}−\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}}\vee\left({x}=\pm\frac{\mathrm{3}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}}\wedge{y}=−{x}\right) \\ $$
Commented by MM42 last updated on 20/Jul/23
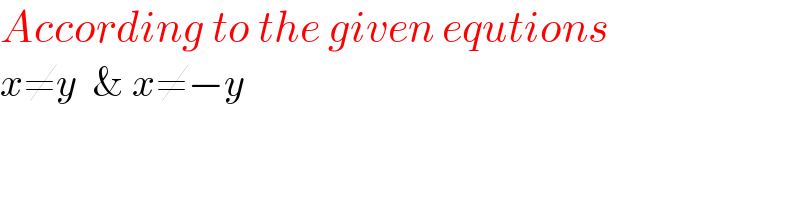
$${According}\:{to}\:{the}\:{given}\:{equtions}\: \\ $$$${x}\neq{y}\:\:\&\:{x}\neq−{y} \\ $$
Commented by Frix last updated on 20/Jul/23
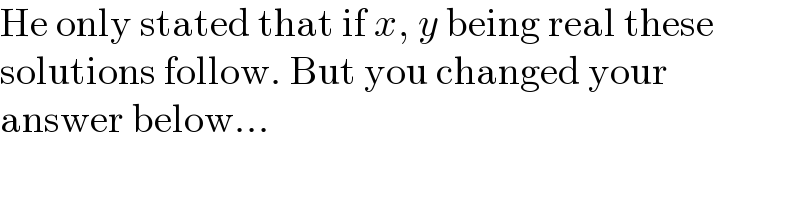
$$\mathrm{He}\:\mathrm{only}\:\mathrm{stated}\:\mathrm{that}\:\mathrm{if}\:{x},\:{y}\:\mathrm{being}\:\mathrm{real}\:\mathrm{these} \\ $$$$\mathrm{solutions}\:\mathrm{follow}.\:\mathrm{But}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{changed}\:\mathrm{your} \\ $$$$\mathrm{answer}\:\mathrm{below}... \\ $$
Answered by MM42 last updated on 20/Jul/23
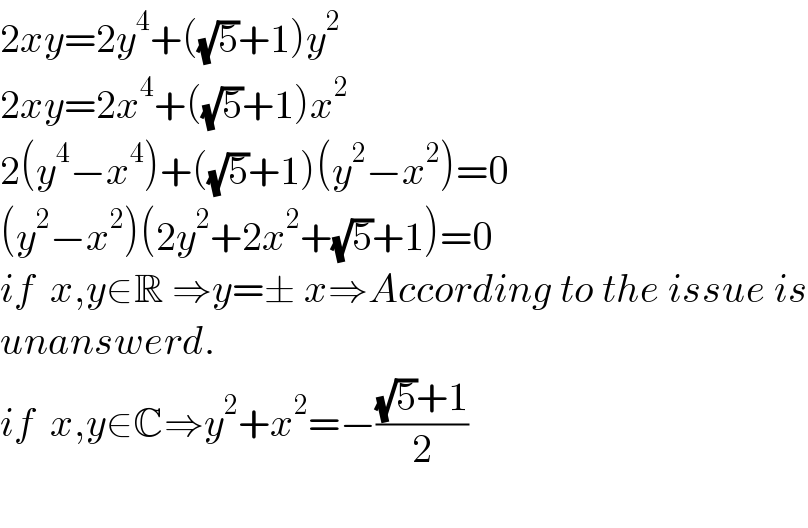
$$\mathrm{2}{xy}=\mathrm{2}{y}^{\mathrm{4}} +\left(\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}+\mathrm{1}\right){y}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}{xy}=\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{4}} +\left(\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}+\mathrm{1}\right){x}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}\left({y}^{\mathrm{4}} −{x}^{\mathrm{4}} \right)+\left(\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}+\mathrm{1}\right)\left({y}^{\mathrm{2}} −{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\left({y}^{\mathrm{2}} −{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\left(\mathrm{2}{y}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}+\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${if}\:\:{x},{y}\in\mathbb{R}\:\Rightarrow{y}=\pm\:{x}\Rightarrow{According}\:{to}\:{the}\:{issue}\:{is} \\ $$$${unanswerd}.\: \\ $$$${if}\:\:{x},{y}\in\mathbb{C}\Rightarrow{y}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}^{\mathrm{2}} =−\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}+\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by MJS_new last updated on 20/Jul/23
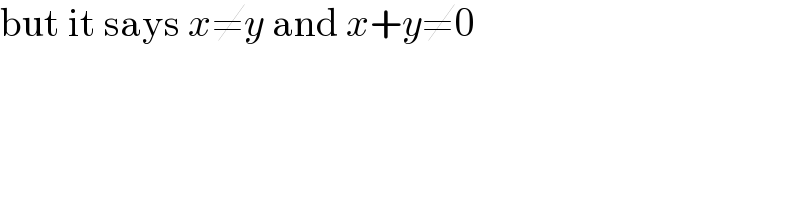
$$\mathrm{but}\:\mathrm{it}\:\mathrm{says}\:{x}\neq{y}\:\mathrm{and}\:{x}+{y}\neq\mathrm{0} \\ $$
