
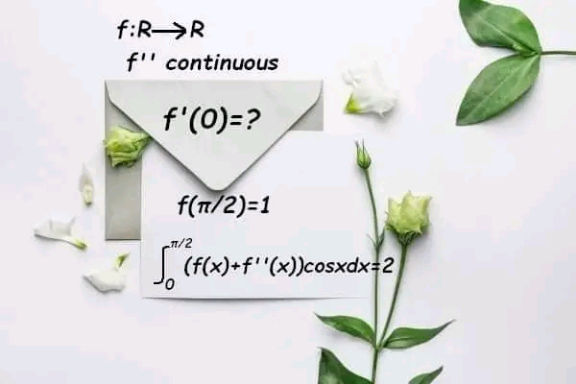
Question Number 194913 by cortano12 last updated on 19/Jul/23
Answered by witcher3 last updated on 19/Jul/23
![(f(x)+f′′(x))cos(x)=g(x) ∫^(π/2) _0 f′′cos(x)dx=f′cos(x)]_0 ^(π/2) +∫f′sin(x)dx =−f′(0)+fsin(x)]_0 ^(π/2) −∫_0 ^(π/2) fcosx)dx ⇔∫_0 ^(π/2) (f+f′′)cos(x)dx=f((π/2))−f′(0)=2 f′(0)=−1](Q194922.png)
$$\left(\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)+\mathrm{f}''\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\right)\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)=\mathrm{g}\left(\mathrm{x}\right) \\ $$$$\left.\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\int}^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \mathrm{f}''\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{dx}=\mathrm{f}'\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} +\int\mathrm{f}'\mathrm{sin}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$\left.=\left.−\mathrm{f}'\left(\mathrm{0}\right)+\mathrm{fsin}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} −\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \mathrm{fcosx}\right)\mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$\Leftrightarrow\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}} \left(\mathrm{f}+\mathrm{f}''\right)\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{dx}=\mathrm{f}\left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\right)−\mathrm{f}'\left(\mathrm{0}\right)=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\mathrm{f}'\left(\mathrm{0}\right)=−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by dimentri last updated on 20/Jul/23
![I=I_1 +I_2 where { ((I_1 =∫_0 ^(π/2) f(x) cos x dx)),((I_2 = ∫_0 ^(π/2) f ′′(x) cos x dx)) :} determinant (( )) I_1 = [ f(x) sin x ]_0 ^(π/2) −∫_0 ^(π/2) f ′(x)sin x dx I_1 = 1−[ (−f ′(x)cos x)_0 ^(π/2) +∫_0 ^(π/2) f^ ′′(x)cos x dx ] I_1 = 1−(0+f ′(0))−∫_0 ^(π/2) f′′(x)cos x dx I_1 = 1−f ′(0)−∫_0 ^(π/2) f ′′(x)cos x dx I = 1−f ′(0)−∫_0 ^(π/2) f ′′(x)cos x dx +∫_0 ^(π/2) f ′′(x) cos x dx = 2 ⇔ 1−f ′(0) = 2 ⇔ determinant (((f ′(0)=−1)))](Q194929.png)
$$\:\:\:\: \\ $$$$ {I}={I}_{\mathrm{1}} +{I}_{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\:{where}\:\begin{cases}{{I}_{\mathrm{1}} =\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\pi/\mathrm{2}} {\int}}{f}\left({x}\right)\:\mathrm{cos}\:{x}\:{dx}}\\{{I}_{\mathrm{2}} =\:\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\pi/\mathrm{2}} {\int}}{f}\:''\left({x}\right)\:\mathrm{cos}\:{x}\:{dx}}\end{cases} \\ $$$$\:\:\begin{array}{|c|}{ }\\\hline\end{array} \\ $$$$\:\:{I}_{\mathrm{1}} =\:\left[\:{f}\left({x}\right)\:\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\:\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\pi/\mathrm{2}} −\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\pi/\mathrm{2}} {\int}}{f}\:'\left({x}\right)\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\:{dx} \\ $$$$\:\:{I}_{\mathrm{1}} =\:\mathrm{1}−\left[\:\left(−{f}\:'\left({x}\right)\mathrm{cos}\:{x}\right)_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\pi/\mathrm{2}} +\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\pi/\mathrm{2}} {\int}}{f}^{\:} ''\left({x}\right)\mathrm{cos}\:{x}\:{dx}\:\right] \\ $$$$\:\:{I}_{\mathrm{1}} =\:\mathrm{1}−\left(\mathrm{0}+{f}\:'\left(\mathrm{0}\right)\right)−\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\pi/\mathrm{2}} {\int}}{f}''\left({x}\right)\mathrm{cos}\:{x}\:{dx} \\ $$$$\:\:{I}_{\mathrm{1}} =\:\mathrm{1}−{f}\:'\left(\mathrm{0}\right)−\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\pi/\mathrm{2}} {\int}}{f}\:''\left({x}\right)\mathrm{cos}\:{x}\:{dx} \\ $$$$\: \:{I}\:=\:\mathrm{1}−{f}\:'\left(\mathrm{0}\right)−\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\pi/\mathrm{2}} {\int}}{f}\:''\left({x}\right)\mathrm{cos}\:{x}\:{dx}\:+\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\pi/\mathrm{2}} {\int}}{f}\:''\left({x}\right)\:\mathrm{cos}\:{x}\:{dx}\:=\:\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\:\:\Leftrightarrow\:\mathrm{1}−{f}\:'\left(\mathrm{0}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\Leftrightarrow\:\begin{array}{|c|}{{f}\:'\left(\mathrm{0}\right)=−\mathrm{1}}\\\hline\end{array} \\ $$
