
Question Number 183761 by MikeH last updated on 29/Dec/22
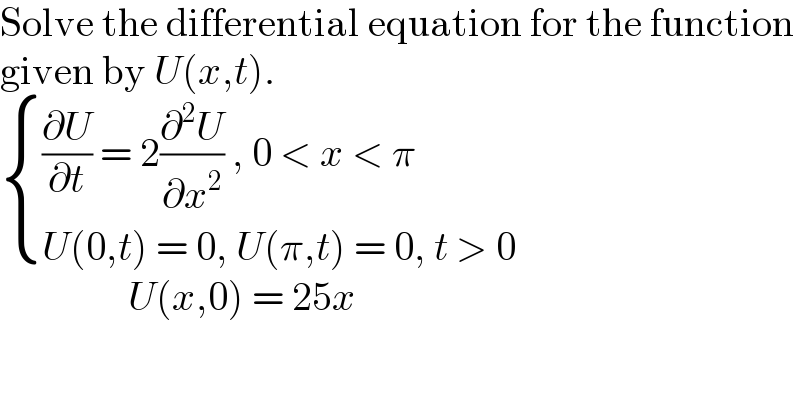
$$\mathrm{Solve}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{differential}\:\mathrm{equation}\:\mathrm{for}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{function} \\ $$ $$\mathrm{given}\:\mathrm{by}\:{U}\left({x},{t}\right). \\ $$ $$\begin{cases}{\frac{\partial{U}}{\partial{t}}\:=\:\mathrm{2}\frac{\partial^{\mathrm{2}} {U}}{\partial{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:,\:\mathrm{0}\:<\:{x}\:<\:\pi}\\{{U}\left(\mathrm{0},{t}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{0},\:{U}\left(\pi,{t}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{0},\:{t}\:>\:\mathrm{0}}\end{cases} \\ $$ $$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{U}\left({x},\mathrm{0}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{25}{x} \\ $$
Answered by leodera last updated on 18/May/23
![take fourier sine transform of both sides F_s {(∂u/∂t)} = 2F_s {(∂^2 u/∂x^2 )} let u_s ^− = ∫_0 ^π u(x,t)sin (sx)dx (d/dt)u_s ^− = 2[−s^2 u_s ^− + s{u(0,t) − (−1)^s u(π,t)}] (d/dt)u_s ^− = −2s^2 u_s ^− solving the D.E u_s ^− = Ae^(−2s^2 t) but u_s ^− (s,0) = ∫_0 ^π 25xsin (sx)dx = −((25π)/s)cos (sπ) u_s ^− (s,0) = Ae^(−2s^2 ×0) = −((25π)/s)cos (sπ) ∴ A = −((25π)/s)cos (sπ) ∴ u_s ^− (s,t) = −((25π)/s)cos (sπ)e^(−2s^2 t) taking inverse fourier transform F^− {u_s ^− (s,t)} = u(x,t) = (2/π)Σ_(s=1) ^∞ −((25π)/s)cos (sπ)e^(−2s^2 t) sin (sx) u(x,t) = −50Σ_(s=1) ^∞ (((−1)^s )/s)e^(−2p^2 t) sin (sx)](Q192435.png)
$${take}\:{fourier}\:{sine}\:{transform}\:{of}\:{both}\:{sides} \\ $$ $$ \\ $$ $$\mathscr{F}_{{s}} \left\{\frac{\partial{u}}{\partial{t}}\right\}\:=\:\mathrm{2}\mathscr{F}_{{s}} \left\{\frac{\partial^{\mathrm{2}} {u}}{\partial{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right\} \\ $$ $${let}\:\overset{−} {{u}}_{{s}} \:=\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\pi} {u}\left({x},{t}\right)\mathrm{sin}\:\left({sx}\right){dx} \\ $$ $$\frac{{d}}{{dt}}\overset{−} {{u}}_{{s}} \:=\:\mathrm{2}\left[−{s}^{\mathrm{2}} \overset{−} {{u}}_{{s}} \:+\:{s}\left\{{u}\left(\mathrm{0},{t}\right)\:−\:\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{s}} {u}\left(\pi,{t}\right)\right\}\right] \\ $$ $$\frac{{d}}{{dt}}\overset{−} {{u}}_{{s}} \:=\:−\mathrm{2}{s}^{\mathrm{2}} \overset{−} {{u}}_{{s}} \\ $$ $${solving}\:{the}\:{D}.{E} \\ $$ $$\overset{−} {{u}}_{{s}} \:=\:{Ae}^{−\mathrm{2}{s}^{\mathrm{2}} {t}} \\ $$ $${but}\:\overset{−} {{u}}_{{s}} \left({s},\mathrm{0}\right)\:=\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\pi} \mathrm{25}{x}\mathrm{sin}\:\left({sx}\right){dx}\: \\ $$ $$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\:−\frac{\mathrm{25}\pi}{{s}}\mathrm{cos}\:\left({s}\pi\right) \\ $$ $$\overset{−} {{u}}_{{s}} \left({s},\mathrm{0}\right)\:=\:{Ae}^{−\mathrm{2}{s}^{\mathrm{2}} ×\mathrm{0}} \:=\:−\frac{\mathrm{25}\pi}{{s}}\mathrm{cos}\:\left({s}\pi\right) \\ $$ $$\therefore\:{A}\:=\:−\frac{\mathrm{25}\pi}{{s}}\mathrm{cos}\:\left({s}\pi\right)\:\:\: \\ $$ $$\therefore\:\overset{−} {{u}}_{{s}} \left({s},{t}\right)\:=\:−\frac{\mathrm{25}\pi}{{s}}\mathrm{cos}\:\left({s}\pi\right){e}^{−\mathrm{2}{s}^{\mathrm{2}} {t}} \\ $$ $$ \\ $$ $${taking}\:{inverse}\:{fourier}\:{transform} \\ $$ $$\mathscr{F}^{−} \left\{\overset{−} {{u}}_{{s}} \left({s},{t}\right)\right\}\:=\:{u}\left({x},{t}\right)\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\pi}\underset{{s}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}−\frac{\mathrm{25}\pi}{{s}}\mathrm{cos}\:\left({s}\pi\right){e}^{−\mathrm{2}{s}^{\mathrm{2}} {t}} \mathrm{sin}\:\left({sx}\right) \\ $$ $${u}\left({x},{t}\right)\:=\:−\mathrm{50}\underset{{s}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{s}} }{{s}}{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{p}^{\mathrm{2}} {t}} \mathrm{sin}\:\left({sx}\right) \\ $$ $$ \\ $$ $$ \\ $$
