
Question Number 167462 by Bagus1003 last updated on 17/Mar/22

$$\mathrm{4}^{{x}} +\mathrm{6}^{{x}} =\mathrm{9}^{{x}} \\ $$$${How}\:{much}\:{the}\:{x}\:{is}? \\ $$
Answered by Jamshidbek last updated on 17/Mar/22
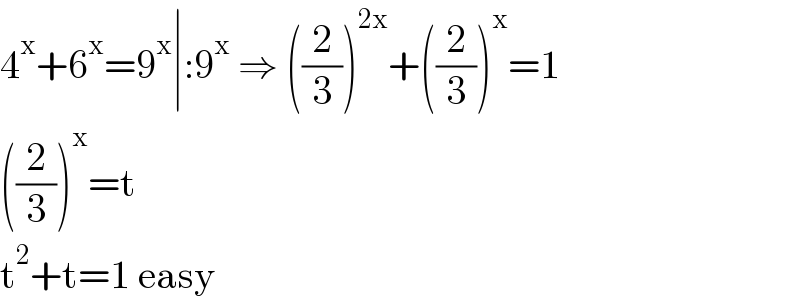
$$\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{x}} +\mathrm{6}^{\mathrm{x}} =\mathrm{9}^{\mathrm{x}} \mid:\mathrm{9}^{\mathrm{x}} \:\Rightarrow\:\left(\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}\right)^{\mathrm{2x}} +\left(\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}\right)^{\mathrm{x}} =\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\left(\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}\right)^{\mathrm{x}} =\mathrm{t} \\ $$$$\mathrm{t}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{t}=\mathrm{1}\:\mathrm{easy} \\ $$
Answered by puissant last updated on 17/Mar/22
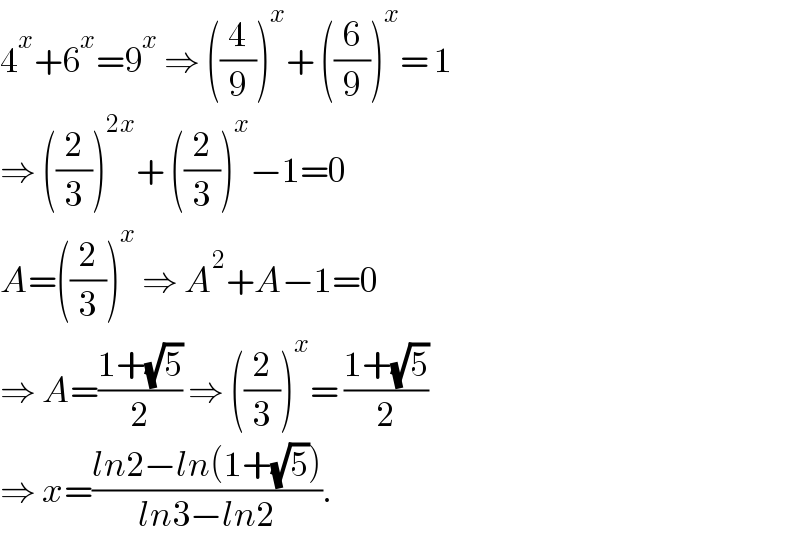
$$\mathrm{4}^{{x}} +\mathrm{6}^{{x}} =\mathrm{9}^{{x}} \:\Rightarrow\:\left(\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{9}}\right)^{{x}} +\:\left(\frac{\mathrm{6}}{\mathrm{9}}\right)^{{x}} =\:\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\left(\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}{x}} +\:\left(\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}\right)^{{x}} −\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${A}=\left(\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}\right)^{{x}} \:\Rightarrow\:{A}^{\mathrm{2}} +{A}−\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:{A}=\frac{\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\Rightarrow\:\left(\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}\right)^{{x}} =\:\frac{\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:{x}=\frac{{ln}\mathrm{2}−{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}\right)}{{ln}\mathrm{3}−{ln}\mathrm{2}}. \\ $$
Commented by Jamshidbek last updated on 17/Mar/22
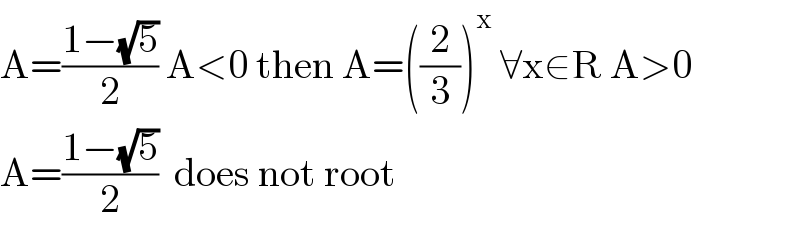
$$\mathrm{A}=\frac{\mathrm{1}−\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\mathrm{A}<\mathrm{0}\:\mathrm{then}\:\mathrm{A}=\left(\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}\right)^{\mathrm{x}} \:\forall\mathrm{x}\in\mathrm{R}\:\mathrm{A}>\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{A}=\frac{\mathrm{1}−\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\:\mathrm{does}\:\mathrm{not}\:\mathrm{root} \\ $$
Commented by MJS_new last updated on 17/Mar/22
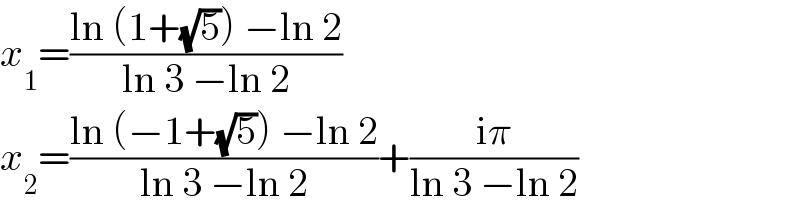
$${x}_{\mathrm{1}} =\frac{\mathrm{ln}\:\left(\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}\right)\:−\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{3}\:−\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${x}_{\mathrm{2}} =\frac{\mathrm{ln}\:\left(−\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}\right)\:−\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{3}\:−\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{2}}+\frac{\mathrm{i}\pi}{\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{3}\:−\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
