
Question Number 166975 by henderson last updated on 03/Mar/22
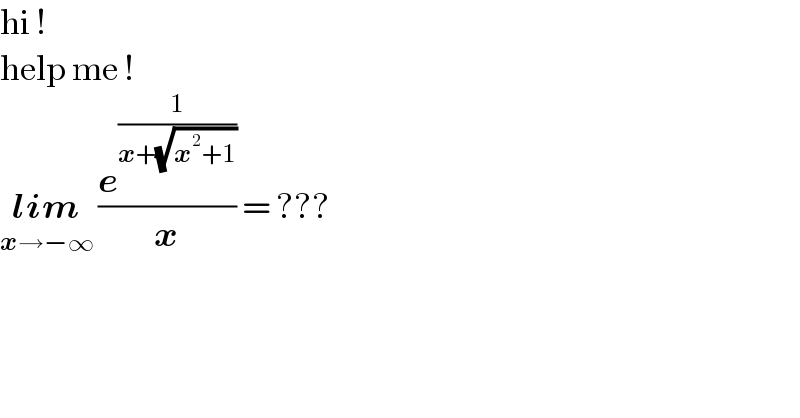
$$\mathrm{hi}\:!\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{help}\:\mathrm{me}\:! \\ $$$$\underset{\boldsymbol{{x}}\rightarrow−\infty} {\boldsymbol{{lim}}}\:\frac{\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\boldsymbol{{x}}+\sqrt{\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}}} }{\boldsymbol{{x}}}\:=\:??? \\ $$
Commented by null last updated on 04/Mar/22

$$\mathrm{no} \\ $$
Commented by henderson last updated on 04/Mar/22

$$\boldsymbol{\mathrm{no}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{answer}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{for}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{this}}\:???\::\left(\right. \\ $$
Commented by MJS_new last updated on 04/Mar/22

$$\mathbb{OBVIOUSLY}!!! \\ $$
Answered by null last updated on 04/Mar/22

$$\mathrm{post}\:\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{1}\:\mathrm{instead}! \\ $$$$\mathrm{this}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{wrong}! \\ $$
Answered by MJS_new last updated on 04/Mar/22
![lim_(x→−∞) (e^(1/(x+(√(x^2 +1)))) /x) = [t=(1/(x+(√(x^2 +1)))) ⇔ x=((1−t^2 )/(2t)); x→−∞ ⇒ t→+∞] =lim_(t→+∞) ((2te^t )/(1−t^2 )) =lim_(t→+∞) (((d^2 /dt^2 )[2te^t ])/((d^2 /dt^2 )[1−t^2 ])) = =lim_(t→+∞) −(t+2)e^t =−∞](Q167017.png)
$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow−\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}+\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}}} }{{x}}\:= \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\left[{t}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}+\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}}\:\Leftrightarrow\:{x}=\frac{\mathrm{1}−{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}{t}};\:{x}\rightarrow−\infty\:\Rightarrow\:{t}\rightarrow+\infty\right] \\ $$$$=\underset{{t}\rightarrow+\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{\mathrm{2}{t}\mathrm{e}^{{t}} }{\mathrm{1}−{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:=\underset{{t}\rightarrow+\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{dt}^{\mathrm{2}} }\left[\mathrm{2}{t}\mathrm{e}^{{t}} \right]}{\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{dt}^{\mathrm{2}} }\left[\mathrm{1}−{t}^{\mathrm{2}} \right]}\:= \\ $$$$=\underset{{t}\rightarrow+\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\:−\left({t}+\mathrm{2}\right)\mathrm{e}^{{t}} \:=−\infty \\ $$
Commented by MJS_new last updated on 04/Mar/22

$$\mathrm{no}\:\mathrm{thank}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{for}\:\mathrm{this}???\::\left(\right. \\ $$
Commented by henderson last updated on 05/Mar/22

$$\mathrm{thank}\:\mathrm{you},\:\mathrm{sir}\:! \\ $$
Commented by MJS_new last updated on 05/Mar/22
��
Answered by Mathspace last updated on 05/Mar/22

$${f}\left({x}\right)=\frac{{e}^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}+\sqrt{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}}} }{{x}}=_{{x}=−{t}} \:\:\frac{{e}^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{−{t}+\sqrt{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}}} }{−{t}} \\ $$$$=−\frac{{e}^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}−{t}}} }{{t}}=−\frac{{e}^{\sqrt{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}+{t}} }{{t}}\left({t}\rightarrow+\infty\right) \\ $$$${let}\:{use}\:{hospital}\:{theorem} \\ $$$${lim}_{{t}\rightarrow+\infty} \frac{{e}^{\sqrt{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}+{t}} }{{t}} \\ $$$$={lim}_{{t}\rightarrow+\infty} \:\:\frac{{d}}{{dt}}\left({e}^{\sqrt{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}+{t}} \right) \\ $$$$={lim}_{{t}\rightarrow+\infty} \:\:\:\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{{t}}{\:\sqrt{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} +{t}}}\right){e}^{\sqrt{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}+{t}} \\ $$$$=+\infty\:\Rightarrow{lim}_{{x}\rightarrow−\infty} {f}\left({x}\right)=−\infty \\ $$
Commented by henderson last updated on 05/Mar/22

$$\mathrm{thank}\:\mathrm{you},\:\mathrm{sir}\:! \\ $$
Commented by henderson last updated on 05/Mar/22
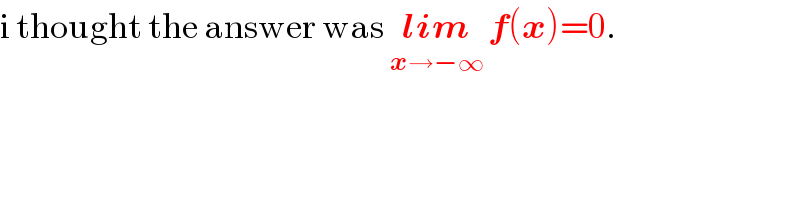
$$\mathrm{i}\:\mathrm{thought}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{answer}\:\mathrm{was}\:\underset{\boldsymbol{{x}}\rightarrow−\infty} {\boldsymbol{{lim}}}\:\boldsymbol{{f}}\left(\boldsymbol{{x}}\right)=\mathrm{0}. \\ $$
