
Question Number 164854 by Zaynal last updated on 22/Jan/22
![Evaluate the Integral; [∫_0 ^∞ ((x^2 − 1)/(1−x)) dx =??] ^({Z.A})](Q164854.png)
$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{Evaluate}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{the}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{Integral}}; \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\left[\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\mathrm{2}} \:−\:\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}−\boldsymbol{{x}}}\:\boldsymbol{{dx}}\:=??\right] \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:^{\left\{\boldsymbol{{Z}}.\mathrm{A}\right\}} \\ $$
Answered by MJS_new last updated on 22/Jan/22
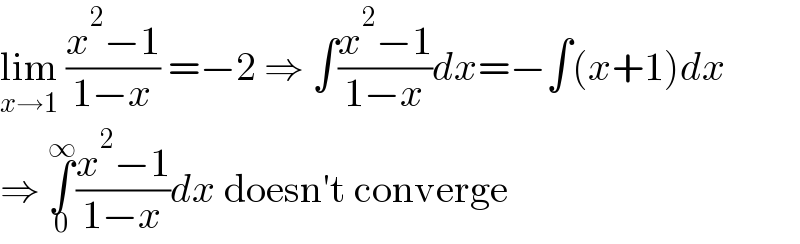
$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}−{x}}\:=−\mathrm{2}\:\Rightarrow\:\int\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}−{x}}{dx}=−\int\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right){dx} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\int}}\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}−{x}}{dx}\:\mathrm{doesn}'\mathrm{t}\:\mathrm{converge} \\ $$
