
Question Number 133757 by liberty last updated on 24/Feb/21

Answered by bobhans last updated on 24/Feb/21
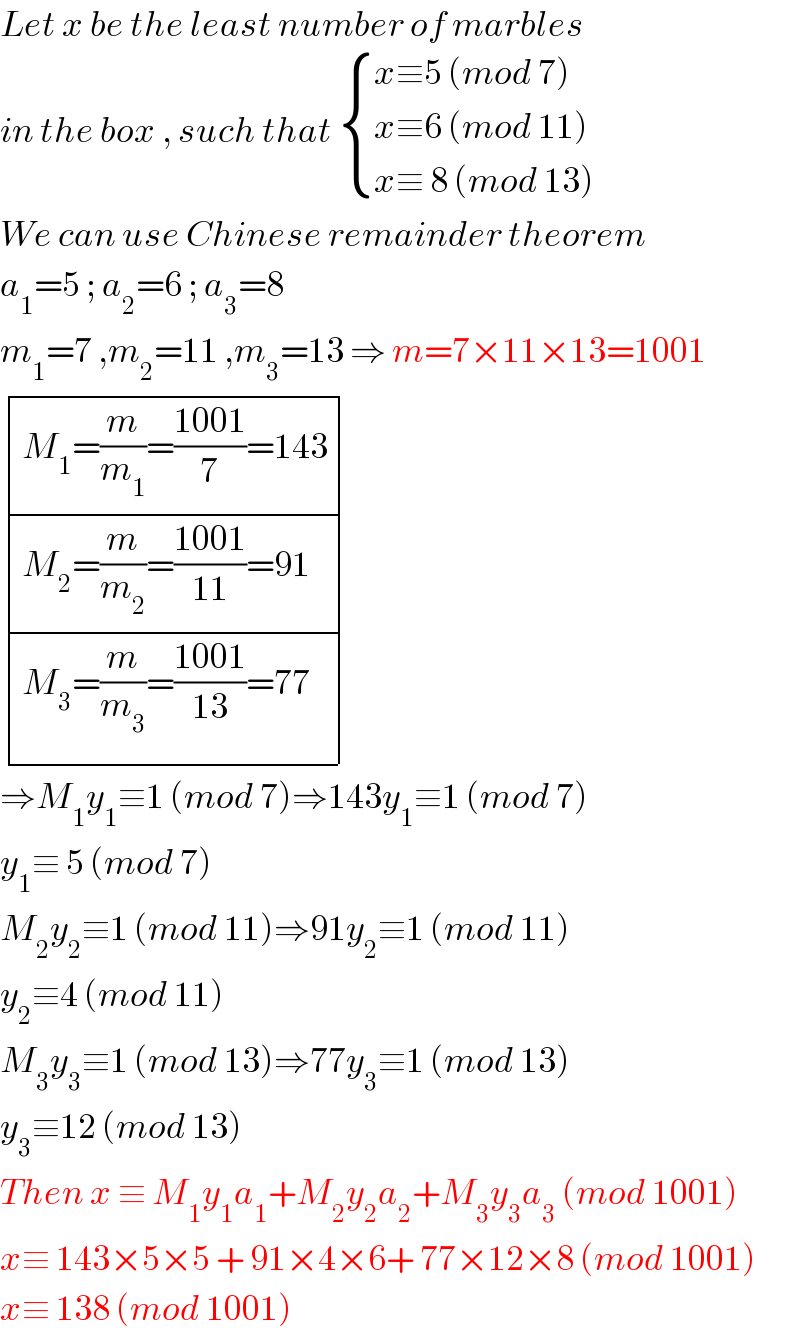
$${Let}\:{x}\:{be}\:{the}\:{least}\:{number}\:{of}\:{marbles} \\ $$$${in}\:{the}\:{box}\:,\:{such}\:{that}\:\begin{cases}{{x}\equiv\mathrm{5}\:\left({mod}\:\mathrm{7}\right)}\\{{x}\equiv\mathrm{6}\:\left({mod}\:\mathrm{11}\right)}\\{{x}\equiv\:\mathrm{8}\:\left({mod}\:\mathrm{13}\right)}\end{cases} \\ $$$${We}\:{can}\:{use}\:{Chinese}\:{remainder}\:{theorem} \\ $$$${a}_{\mathrm{1}} =\mathrm{5}\:;\:{a}_{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{6}\:;\:{a}_{\mathrm{3}} =\mathrm{8} \\ $$$${m}_{\mathrm{1}} =\mathrm{7}\:,{m}_{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{11}\:,{m}_{\mathrm{3}} =\mathrm{13}\:\Rightarrow\:{m}=\mathrm{7}×\mathrm{11}×\mathrm{13}=\mathrm{1001} \\ $$$$\begin{array}{|c|c|c|}{{M}_{\mathrm{1}} =\frac{{m}}{{m}_{\mathrm{1}} }=\frac{\mathrm{1001}}{\mathrm{7}}=\mathrm{143}}\\{{M}_{\mathrm{2}} =\frac{{m}}{{m}_{\mathrm{2}} }=\frac{\mathrm{1001}}{\mathrm{11}}=\mathrm{91}}\\{{M}_{\mathrm{3}} =\frac{{m}}{{m}_{\mathrm{3}} }=\frac{\mathrm{1001}}{\mathrm{13}}=\mathrm{77}}\\\hline\end{array} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{M}_{\mathrm{1}} {y}_{\mathrm{1}} \equiv\mathrm{1}\:\left({mod}\:\mathrm{7}\right)\Rightarrow\mathrm{143}{y}_{\mathrm{1}} \equiv\mathrm{1}\:\left({mod}\:\mathrm{7}\right) \\ $$$${y}_{\mathrm{1}} \equiv\:\mathrm{5}\:\left({mod}\:\mathrm{7}\right) \\ $$$${M}_{\mathrm{2}} {y}_{\mathrm{2}} \equiv\mathrm{1}\:\left({mod}\:\mathrm{11}\right)\Rightarrow\mathrm{91}{y}_{\mathrm{2}} \equiv\mathrm{1}\:\left({mod}\:\mathrm{11}\right) \\ $$$${y}_{\mathrm{2}} \equiv\mathrm{4}\:\left({mod}\:\mathrm{11}\right) \\ $$$${M}_{\mathrm{3}} {y}_{\mathrm{3}} \equiv\mathrm{1}\:\left({mod}\:\mathrm{13}\right)\Rightarrow\mathrm{77}{y}_{\mathrm{3}} \equiv\mathrm{1}\:\left({mod}\:\mathrm{13}\right) \\ $$$${y}_{\mathrm{3}} \equiv\mathrm{12}\:\left({mod}\:\mathrm{13}\right) \\ $$$${Then}\:{x}\:\equiv\:{M}_{\mathrm{1}} {y}_{\mathrm{1}} {a}_{\mathrm{1}} +{M}_{\mathrm{2}} {y}_{\mathrm{2}} {a}_{\mathrm{2}} +{M}_{\mathrm{3}} {y}_{\mathrm{3}} {a}_{\mathrm{3}} \:\left({mod}\:\mathrm{1001}\right) \\ $$$${x}\equiv\:\mathrm{143}×\mathrm{5}×\mathrm{5}\:+\:\mathrm{91}×\mathrm{4}×\mathrm{6}+\:\mathrm{77}×\mathrm{12}×\mathrm{8}\:\left({mod}\:\mathrm{1001}\right) \\ $$$${x}\equiv\:\mathrm{138}\:\left({mod}\:\mathrm{1001}\right) \\ $$
