
Question Number 128334 by liberty last updated on 06/Jan/21
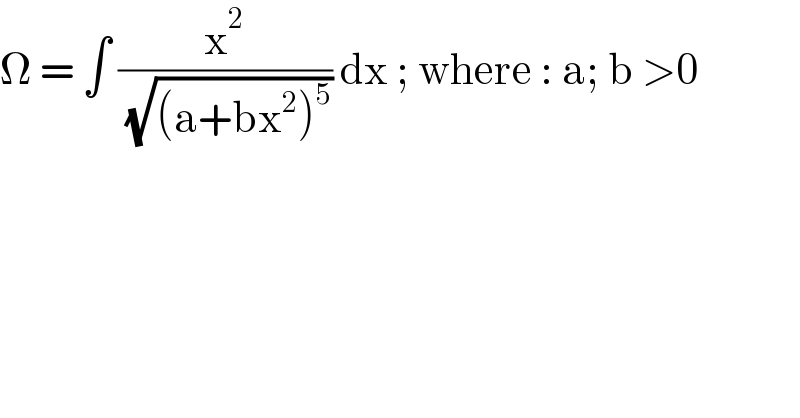
$$\Omega\:=\:\int\:\frac{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\:\sqrt{\left(\mathrm{a}+\mathrm{bx}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)^{\mathrm{5}} }}\:\mathrm{dx}\:;\:\mathrm{where}\::\:\mathrm{a};\:\mathrm{b}\:>\mathrm{0}\: \\ $$
Answered by bramlexs22 last updated on 06/Jan/21
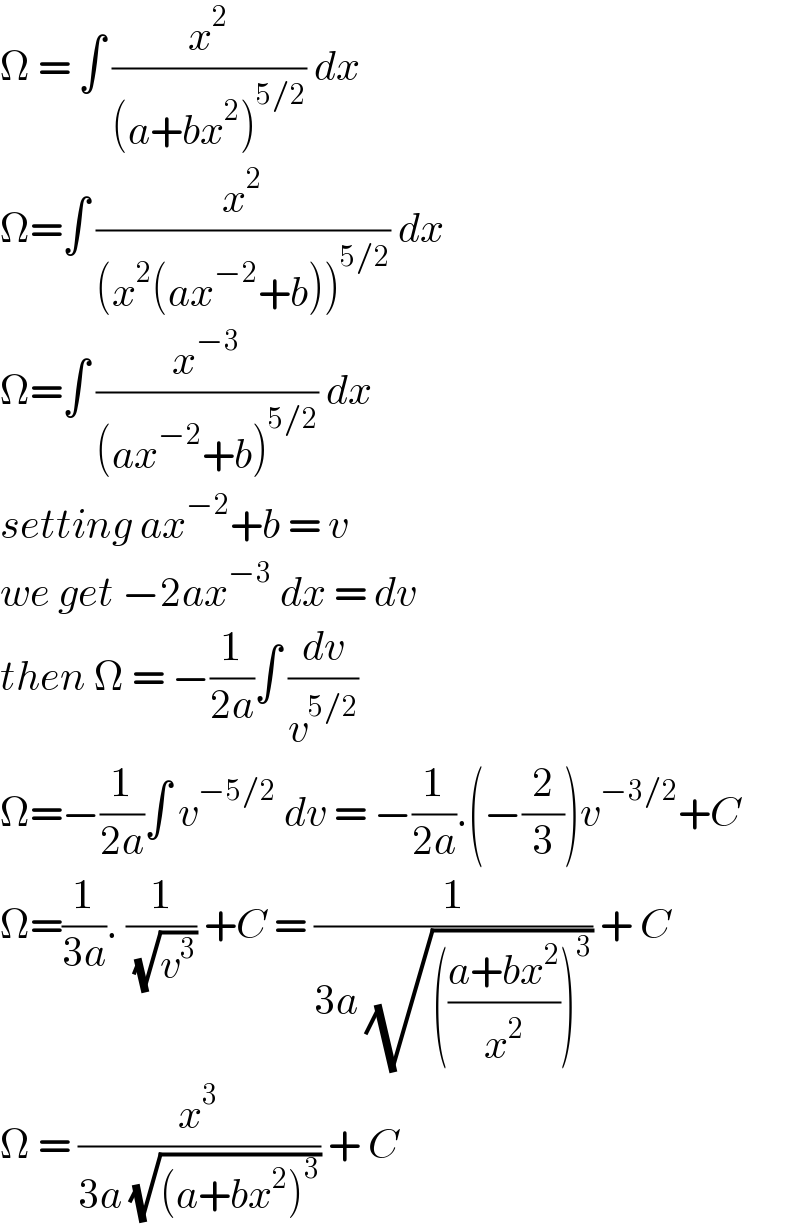
$$\Omega\:=\:\int\:\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\left({a}+{bx}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)^{\mathrm{5}/\mathrm{2}} }\:{dx}\: \\ $$ $$\Omega=\int\:\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} \left({ax}^{−\mathrm{2}} +{b}\right)\right)^{\mathrm{5}/\mathrm{2}} }\:{dx} \\ $$ $$\Omega=\int\:\frac{{x}^{−\mathrm{3}} }{\left({ax}^{−\mathrm{2}} +{b}\right)^{\mathrm{5}/\mathrm{2}} }\:{dx} \\ $$ $${setting}\:{ax}^{−\mathrm{2}} +{b}\:=\:{v}\: \\ $$ $${we}\:{get}\:−\mathrm{2}{ax}^{−\mathrm{3}} \:{dx}\:=\:{dv}\: \\ $$ $${then}\:\Omega\:=\:−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{a}}\int\:\frac{{dv}}{{v}^{\mathrm{5}/\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$ $$\Omega=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{a}}\int\:{v}^{−\mathrm{5}/\mathrm{2}} \:{dv}\:=\:−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{a}}.\left(−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}\right){v}^{−\mathrm{3}/\mathrm{2}} +{C} \\ $$ $$\Omega=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}{a}}.\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{{v}^{\mathrm{3}} }}\:+{C}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}{a}\:\sqrt{\left(\frac{{a}+{bx}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)^{\mathrm{3}} }}\:+\:{C} \\ $$ $$\Omega\:=\:\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{3}{a}\:\sqrt{\left({a}+{bx}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)^{\mathrm{3}} }}\:+\:{C}\: \\ $$
