
Previous in Differential Equation Next in Differential Equation
Question Number 116105 by ShakaLaka last updated on 30/Sep/20
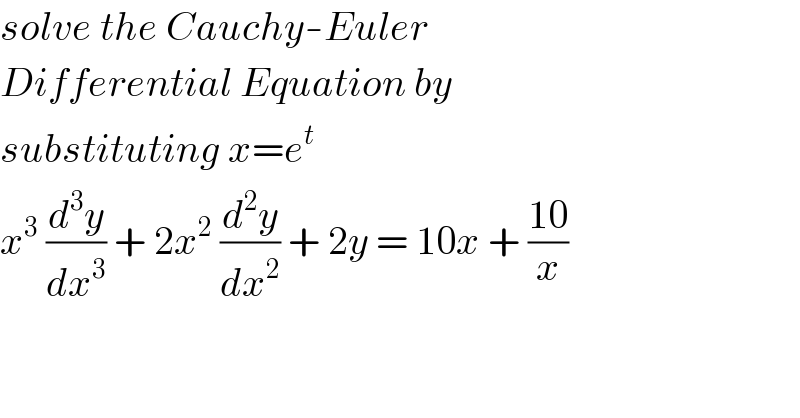
$${solve}\:{the}\:{Cauchy}-{Euler}\: \\ $$$${Differential}\:{Equation}\:{by} \\ $$$${substituting}\:{x}={e}^{{t}} \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{3}} \:\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{3}} {y}}{{dx}^{\mathrm{3}} }\:+\:\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}}{{dx}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:+\:\mathrm{2}{y}\:=\:\mathrm{10}{x}\:+\:\frac{\mathrm{10}}{{x}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by TANMAY PANACEA last updated on 01/Oct/20
![x=e^t →(dx/dt)=e^t (dy/dx)=(dy/dt)×(dt/dx)=(dy/dt)×(1/e^t )→e^t (dy/dx)=(dy/dt)→x(dy/dx)=(dy/dt)← (d/dx)(x(dy/dx))=(d/dt)((dy/dt))×(dt/dx) (x(d^2 y/dx^2 )+(dy/dx))×(dx/dt)=(d^2 y/dt^2 ) x(x(d^2 y/dx^2 )+(dy/dx))=(d^2 y/dt^2 ) x^2 (d^2 y/dx^2 )=(d^2 y/dt^2 )−(dy/dt)← (d/dx)(x^2 (d^2 y/dx^2 ))=(d/dt)((d^2 y/dt^2 )−(dy/dt))×(dt/dx) (x^2 (d^3 y/dx^3 )+2x.(d^2 y/dx^2 ))×(dx/dt)=(d^3 y/dt^3 )−(d^2 y/dt^2 ) x^3 (d^3 y/dx^3 )+2x^2 (d^2 y/dx^2 )=(d^3 y/dt^3 )−(d^2 y/dt^2 ) ★ so (d^3 y/dt^3 )−(d^2 y/dt^2 )+2y=10e^t +10e^(−t) now to be solved C.F m^3 −m^2 +2=0 =m^3 +m^2 −2m^2 −2m+2m+2 =m^2 (m+1) −2m (m+1) +2 (m+1) =(m+1)(m^2 −2m+2) m+1=0 m=−1 m^2 −2m+2=0 m=((2±(√(4−8)))/2)=((2±2i)/2)=1±i so m=−1,1±i C.F y=C_1 e^(−t) +C_2 e^((1+i)t) +C_3 e^((1−i)t) P.I correction pls(in black ) y=((10e^t )/(D^3 −D^2 +2))+((10e^(−t) )/(D^3 −D^2 +2)) [D=(d/dt)] (y/(10))=(e^t /(1−1+2))+(e^(−t) /((D+1)(D^2 −2D+2))) =(e^t /2)+(e^(−t) /((D−1+1){(−1)^2 −2(−1)+2})) =(e^t /2)+(e^(−t) /5)×(1/D) =(e^t /2)+(e^(−t) /5)×t y=C.F+P.I y=C_1 e^(−t) +C_2 e^((1+i)t) +C_3 e^((1−i)t) +[(e^t /2)+(e^(−t) /5)×t]×10 =C_1 x^(−1) +C_2 x^(1+i) +C_3 x^(1−i) +((5x)/1)+((2x^(−1) )/)×lnx](Q116151.png)
$${x}={e}^{{t}} \rightarrow\frac{{dx}}{{dt}}={e}^{{t}} \\ $$$$\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}=\frac{{dy}}{{dt}}×\frac{{dt}}{{dx}}=\frac{{dy}}{{dt}}×\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{e}^{{t}} }\rightarrow{e}^{{t}} \frac{{dy}}{{dx}}=\frac{{dy}}{{dt}}\rightarrow{x}\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}=\frac{{dy}}{{dt}}\leftarrow \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\frac{{d}}{{dx}}\left({x}\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}\right)=\frac{{d}}{{dt}}\left(\frac{{dy}}{{dt}}\right)×\frac{{dt}}{{dx}} \\ $$$$\left({x}\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}}{{dx}^{\mathrm{2}} }+\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}\right)×\frac{{dx}}{{dt}}=\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}}{{dt}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$${x}\left({x}\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}}{{dx}^{\mathrm{2}} }+\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}\right)=\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}}{{dt}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} \frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}}{{dx}^{\mathrm{2}} }=\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}}{{dt}^{\mathrm{2}} }−\frac{{dy}}{{dt}}\leftarrow \\ $$$$\frac{{d}}{{dx}}\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} \frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}}{{dx}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)=\frac{{d}}{{dt}}\left(\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}}{{dt}^{\mathrm{2}} }−\frac{{dy}}{{dt}}\right)×\frac{{dt}}{{dx}} \\ $$$$\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} \frac{{d}^{\mathrm{3}} {y}}{{dx}^{\mathrm{3}} }+\mathrm{2}{x}.\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}}{{dx}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)×\frac{{dx}}{{dt}}=\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{3}} {y}}{{dt}^{\mathrm{3}} }−\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}}{{dt}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{3}} \frac{{d}^{\mathrm{3}} {y}}{{dx}^{\mathrm{3}} }+\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}}{{dx}^{\mathrm{2}} }=\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{3}} {y}}{{dt}^{\mathrm{3}} }−\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}}{{dt}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\bigstar \\ $$$${so} \\ $$$$\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{3}} {y}}{{dt}^{\mathrm{3}} }−\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}}{{dt}^{\mathrm{2}} }+\mathrm{2}{y}=\mathrm{10}{e}^{{t}} +\mathrm{10}{e}^{−{t}} \\ $$$${now}\:{to}\:{be}\:{solved} \\ $$$${C}.{F} \\ $$$${m}^{\mathrm{3}} −{m}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$={m}^{\mathrm{3}} +{m}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}{m}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}{m}+\mathrm{2}{m}+\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$={m}^{\mathrm{2}} \left({m}+\mathrm{1}\right)\:\:−\mathrm{2}{m}\:\left({m}+\mathrm{1}\right)\:\:+\mathrm{2}\:\left({m}+\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$=\left({m}+\mathrm{1}\right)\left({m}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}{m}+\mathrm{2}\right) \\ $$$${m}+\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{0}\:\:{m}=−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${m}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}{m}+\mathrm{2}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${m}=\frac{\mathrm{2}\pm\sqrt{\mathrm{4}−\mathrm{8}}}{\mathrm{2}}=\frac{\mathrm{2}\pm\mathrm{2}{i}}{\mathrm{2}}=\mathrm{1}\pm{i} \\ $$$${so}\:{m}=−\mathrm{1},\mathrm{1}\pm{i} \\ $$$${C}.{F} \\ $$$${y}={C}_{\mathrm{1}} {e}^{−{t}} +{C}_{\mathrm{2}} {e}^{\left(\mathrm{1}+{i}\right){t}} +{C}_{\mathrm{3}} {e}^{\left(\mathrm{1}−{i}\right){t}} \\ $$$${P}.{I} \\ $$$${correction}\:{pls}\left({in}\:{black}\:\right) \\ $$$${y}=\frac{\mathrm{10}{e}^{{t}} }{{D}^{\mathrm{3}} −{D}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}}+\frac{\mathrm{10}{e}^{−{t}} }{{D}^{\mathrm{3}} −{D}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}}\:\:\left[{D}=\frac{{d}}{{dt}}\right] \\ $$$$\frac{{y}}{\mathrm{10}}=\frac{{e}^{{t}} }{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{2}}+\frac{{e}^{−{t}} }{\left({D}+\mathrm{1}\right)\left({D}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}{D}+\mathrm{2}\right)} \\ $$$$=\frac{{e}^{{t}} }{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{{e}^{−{t}} }{\left({D}−\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{1}\right)\left\{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)+\mathrm{2}\right\}} \\ $$$$=\frac{{e}^{{t}} }{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{{e}^{−{t}} }{\mathrm{5}}×\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{D}} \\ $$$$=\frac{{e}^{{t}} }{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{{e}^{−{t}} }{\mathrm{5}}×{t} \\ $$$${y}={C}.{F}+{P}.{I} \\ $$$${y}={C}_{\mathrm{1}} {e}^{−{t}} +{C}_{\mathrm{2}} {e}^{\left(\mathrm{1}+{i}\right){t}} +{C}_{\mathrm{3}} {e}^{\left(\mathrm{1}−{i}\right){t}} +\left[\frac{{e}^{{t}} }{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{{e}^{−{t}} }{\mathrm{5}}×{t}\right]×\mathrm{10} \\ $$$$={C}_{\mathrm{1}} {x}^{−\mathrm{1}} +{C}_{\mathrm{2}} {x}^{\mathrm{1}+{i}} +{C}_{\mathrm{3}} {x}^{\mathrm{1}−{i}} +\frac{\mathrm{5}{x}}{\mathrm{1}}+\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}^{−\mathrm{1}} }{}×{lnx} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by ShakaLaka last updated on 01/Oct/20
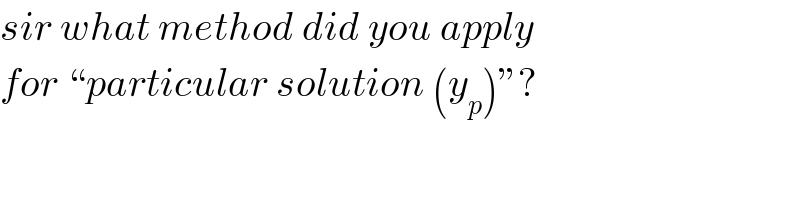
$${sir}\:{what}\:{method}\:{did}\:{you}\:{apply} \\ $$$${for}\:``{particular}\:{solution}\:\left({y}_{{p}} \right)''? \\ $$
Commented by ShakaLaka last updated on 01/Oct/20

$${sir}\:{can}\:{we}\:{apply}\:{mothod}\:{of} \\ $$$${undetermined}\:{coeffitient}?\:{if} \\ $$$${yes}\:{then}\:{what}\:{will}\:{we}\:{take}\:{for} \\ $$$${y}_{{p}} \:{for}\:{the}\:{R}.{H}.{S}\: \\ $$$$``\mathrm{10}{e}^{{t}} \:+\:\mathrm{10}{e}^{−{t}} '' \\ $$
Commented by TANMAY PANACEA last updated on 01/Oct/20

$${i}\:{forgot}\:{to}\:{put}\:\mathrm{10}... \\ $$$${later}\:{corrected} \\ $$
Commented by ShakaLaka last updated on 04/Oct/20
$$\left.{oh}\:{ok}\:{I}\:{got}\:{it}.\:{Thank}\:{you}\::\right) \\ $$
Answered by mindispower last updated on 01/Oct/20
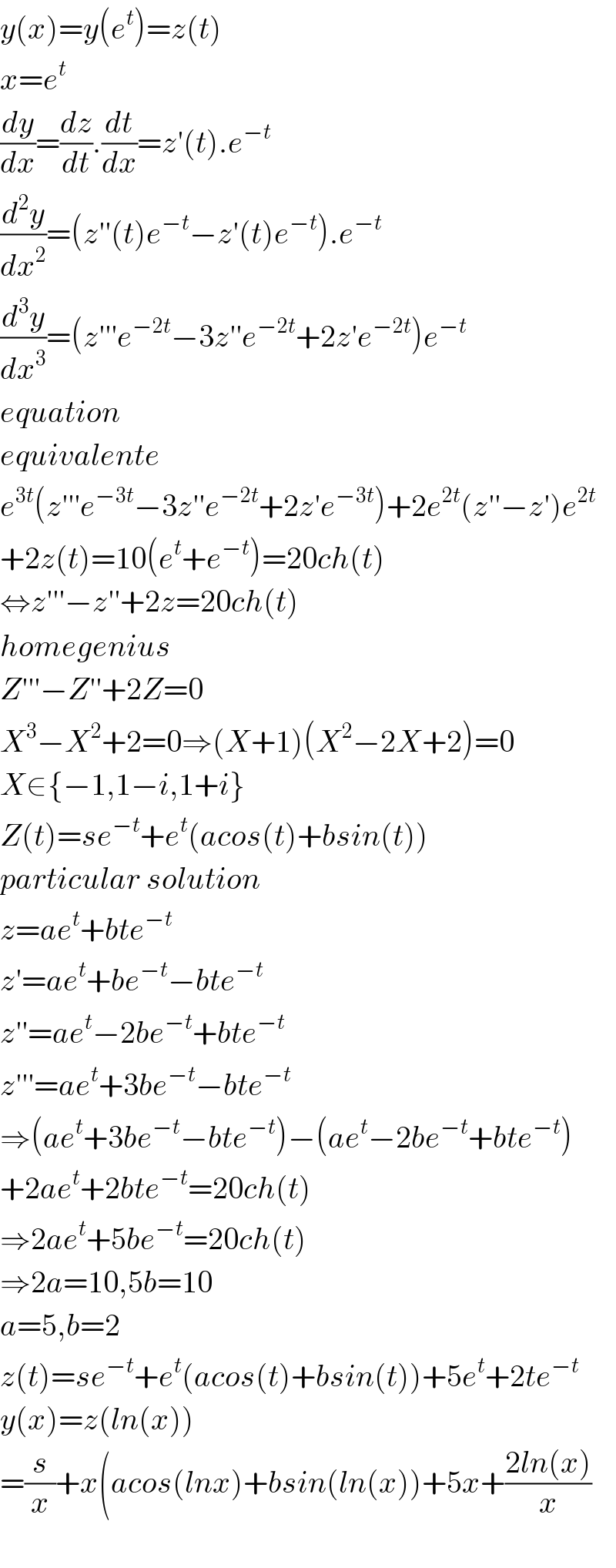
$${y}\left({x}\right)={y}\left({e}^{{t}} \right)={z}\left({t}\right) \\ $$$${x}={e}^{{t}} \\ $$$$\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}=\frac{{dz}}{{dt}}.\frac{{dt}}{{dx}}={z}'\left({t}\right).{e}^{−{t}} \\ $$$$\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}}{{dx}^{\mathrm{2}} }=\left({z}''\left({t}\right){e}^{−{t}} −{z}'\left({t}\right){e}^{−{t}} \right).{e}^{−{t}} \\ $$$$\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{3}} {y}}{{dx}^{\mathrm{3}} }=\left({z}'''{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{t}} −\mathrm{3}{z}''{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{t}} +\mathrm{2}{z}'{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{t}} \right){e}^{−{t}} \\ $$$${equation} \\ $$$${equivalente} \\ $$$${e}^{\mathrm{3}{t}} \left({z}'''{e}^{−\mathrm{3}{t}} −\mathrm{3}{z}''{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{t}} +\mathrm{2}{z}'{e}^{−\mathrm{3}{t}} \right)+\mathrm{2}{e}^{\mathrm{2}{t}} \left({z}''−{z}'\right){e}^{\mathrm{2}{t}} \\ $$$$+\mathrm{2}{z}\left({t}\right)=\mathrm{10}\left({e}^{{t}} +{e}^{−{t}} \right)=\mathrm{20}{ch}\left({t}\right) \\ $$$$\Leftrightarrow{z}'''−{z}''+\mathrm{2}{z}=\mathrm{20}{ch}\left({t}\right) \\ $$$${homegenius} \\ $$$${Z}'''−{Z}''+\mathrm{2}{Z}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${X}^{\mathrm{3}} −{X}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}=\mathrm{0}\Rightarrow\left({X}+\mathrm{1}\right)\left({X}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}{X}+\mathrm{2}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${X}\in\left\{−\mathrm{1},\mathrm{1}−{i},\mathrm{1}+{i}\right\} \\ $$$${Z}\left({t}\right)={se}^{−{t}} +{e}^{{t}} \left({acos}\left({t}\right)+{bsin}\left({t}\right)\right) \\ $$$${particular}\:{solution}\: \\ $$$${z}={ae}^{{t}} +{bte}^{−{t}} \\ $$$${z}'={ae}^{{t}} +{be}^{−{t}} −{bte}^{−{t}} \\ $$$${z}''={ae}^{{t}} −\mathrm{2}{be}^{−{t}} +{bte}^{−{t}} \\ $$$${z}'''={ae}^{{t}} +\mathrm{3}{be}^{−{t}} −{bte}^{−{t}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\left({ae}^{{t}} +\mathrm{3}{be}^{−{t}} −{bte}^{−{t}} \right)−\left({ae}^{{t}} −\mathrm{2}{be}^{−{t}} +{bte}^{−{t}} \right) \\ $$$$+\mathrm{2}{ae}^{{t}} +\mathrm{2}{bte}^{−{t}} =\mathrm{20}{ch}\left({t}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{2}{ae}^{{t}} +\mathrm{5}{be}^{−{t}} =\mathrm{20}{ch}\left({t}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{2}{a}=\mathrm{10},\mathrm{5}{b}=\mathrm{10} \\ $$$${a}=\mathrm{5},{b}=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${z}\left({t}\right)={se}^{−{t}} +{e}^{{t}} \left({acos}\left({t}\right)+{bsin}\left({t}\right)\right)+\mathrm{5}{e}^{{t}} +\mathrm{2}{te}^{−{t}} \\ $$$${y}\left({x}\right)={z}\left({ln}\left({x}\right)\right) \\ $$$$=\frac{{s}}{{x}}+{x}\left({acos}\left({lnx}\right)+{bsin}\left({ln}\left({x}\right)\right)+\mathrm{5}{x}+\frac{\mathrm{2}{ln}\left({x}\right)}{{x}}\right. \\ $$$$ \\ $$
