
Question Number 115472 by Khalmohmmad last updated on 26/Sep/20
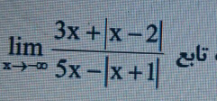
Commented by malwaan last updated on 26/Sep/20
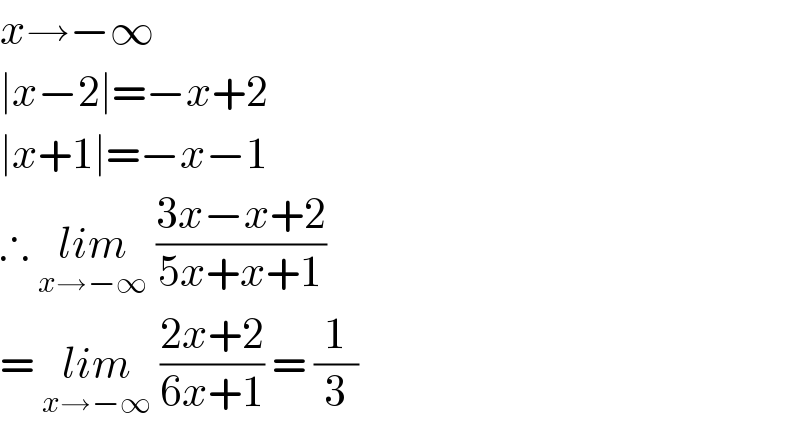
$${x}\rightarrow−\infty \\ $$$$\mid{x}−\mathrm{2}\mid=−{x}+\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\mid{x}+\mathrm{1}\mid=−{x}−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\therefore\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow−\infty} {{lim}}\:\frac{\mathrm{3}{x}−{x}+\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{5}{x}+{x}+\mathrm{1}}\: \\ $$$$=\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow−\infty} {{lim}}\:\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{6}{x}+\mathrm{1}}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$
Answered by bemath last updated on 26/Sep/20
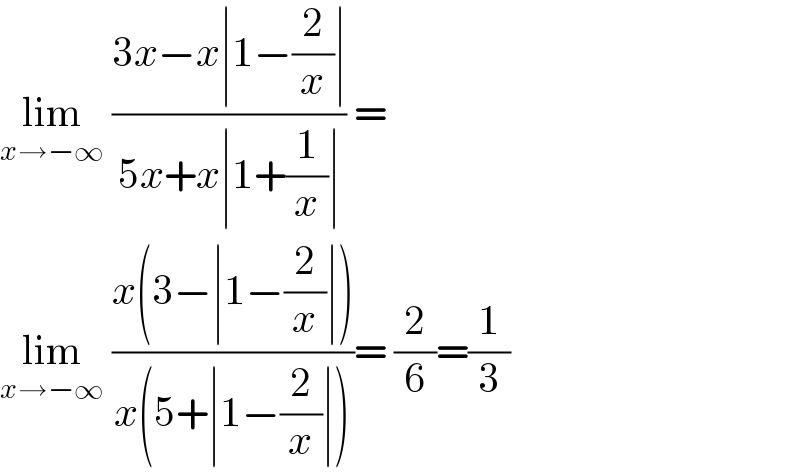
$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow−\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{\mathrm{3}{x}−{x}\mid\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{x}}\mid}{\mathrm{5}{x}+{x}\mid\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\mid}\:= \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow−\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{{x}\left(\mathrm{3}−\mid\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{x}}\mid\right)}{{x}\left(\mathrm{5}+\mid\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{x}}\mid\right)}=\:\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{6}}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$
