
Question Number 114072 by Lordose last updated on 17/Sep/20
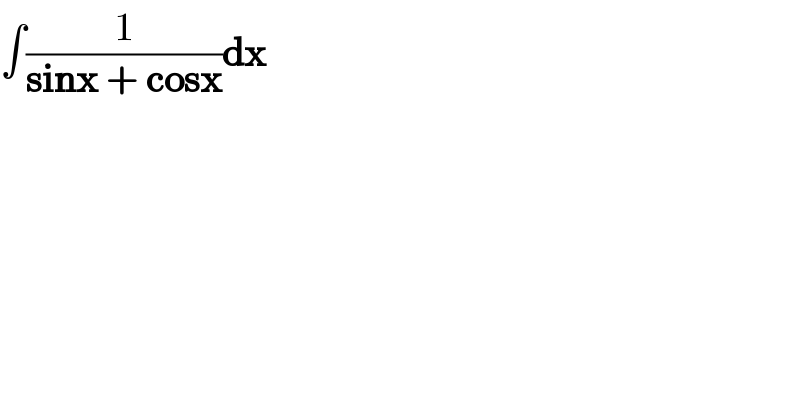
$$\int\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\boldsymbol{\mathrm{sinx}}\:+\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{cosx}}}\boldsymbol{\mathrm{dx}} \\ $$
Answered by Olaf last updated on 17/Sep/20
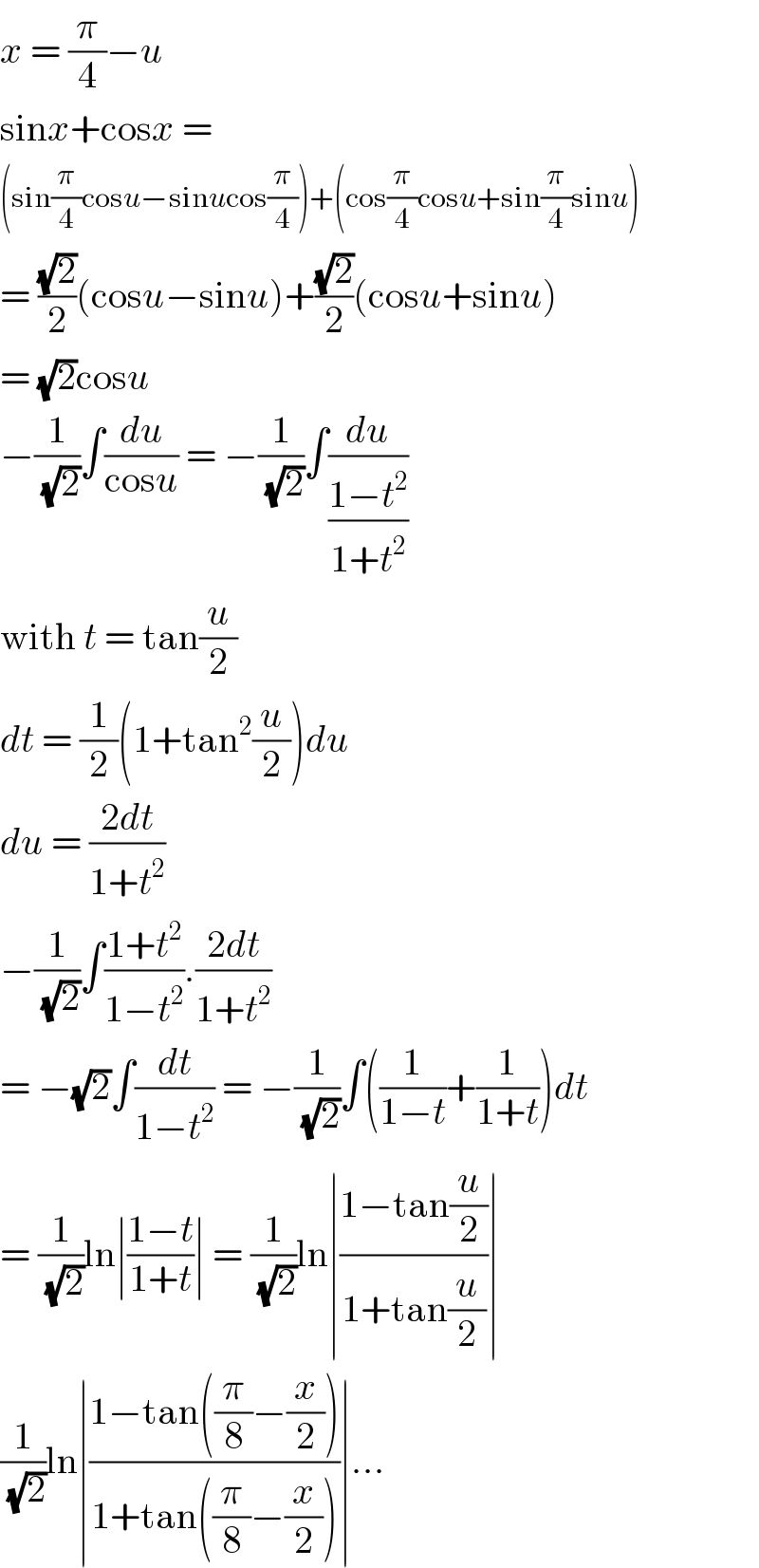
$${x}\:=\:\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}−{u} \\ $$$$\mathrm{sin}{x}+\mathrm{cos}{x}\:=\: \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{sin}\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}\mathrm{cos}{u}−\mathrm{sin}{u}\mathrm{cos}\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}\right)+\left(\mathrm{cos}\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}\mathrm{cos}{u}+\mathrm{sin}\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}\mathrm{sin}{u}\right) \\ $$$$=\:\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{\mathrm{2}}\left(\mathrm{cos}{u}−\mathrm{sin}{u}\right)+\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{\mathrm{2}}\left(\mathrm{cos}{u}+\mathrm{sin}{u}\right) \\ $$$$=\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{cos}{u} \\ $$$$−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\int\frac{{du}}{\mathrm{cos}{u}}\:=\:−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\int\frac{{du}}{\frac{\mathrm{1}−{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{1}+{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }} \\ $$$$\mathrm{with}\:{t}\:=\:\mathrm{tan}\frac{{u}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${dt}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{tan}^{\mathrm{2}} \frac{{u}}{\mathrm{2}}\right){du} \\ $$$${du}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{2}{dt}}{\mathrm{1}+{t}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\int\frac{\mathrm{1}+{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{1}−{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }.\frac{\mathrm{2}{dt}}{\mathrm{1}+{t}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$=\:−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\int\frac{{dt}}{\mathrm{1}−{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:=\:−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\int\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}−{t}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{t}}\right){dt} \\ $$$$=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\mathrm{ln}\mid\frac{\mathrm{1}−{t}}{\mathrm{1}+{t}}\mid\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\mathrm{ln}\mid\frac{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{tan}\frac{{u}}{\mathrm{2}}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{tan}\frac{{u}}{\mathrm{2}}}\mid \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\mathrm{ln}\mid\frac{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{tan}\left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{8}}−\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{tan}\left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{8}}−\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)}\mid... \\ $$
Answered by MJS_new last updated on 17/Sep/20
![∫(dx/(sin x +cos x))= [t=x+(π/4) → dx=dt] =((√2)/2)∫csc t dt=((√2)/2)ln ∣tan (t/2)∣= =((√2)/2)ln ∣tan ((x/2)+(π/8))∣= =((√2)/2)ln ∣(((√2)+2sin x)/( (√2)+2cos x))∣ +C](Q114120.png)
$$\int\frac{{dx}}{\mathrm{sin}\:{x}\:+\mathrm{cos}\:{x}}= \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\left[{t}={x}+\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}\:\rightarrow\:{dx}={dt}\right] \\ $$$$=\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{\mathrm{2}}\int\mathrm{csc}\:{t}\:{dt}=\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{ln}\:\mid\mathrm{tan}\:\frac{{t}}{\mathrm{2}}\mid= \\ $$$$=\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{ln}\:\mid\mathrm{tan}\:\left(\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{8}}\right)\mid= \\ $$$$=\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{ln}\:\mid\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}+\mathrm{2sin}\:{x}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}+\mathrm{2cos}\:{x}}\mid\:+{C} \\ $$
Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 17/Sep/20
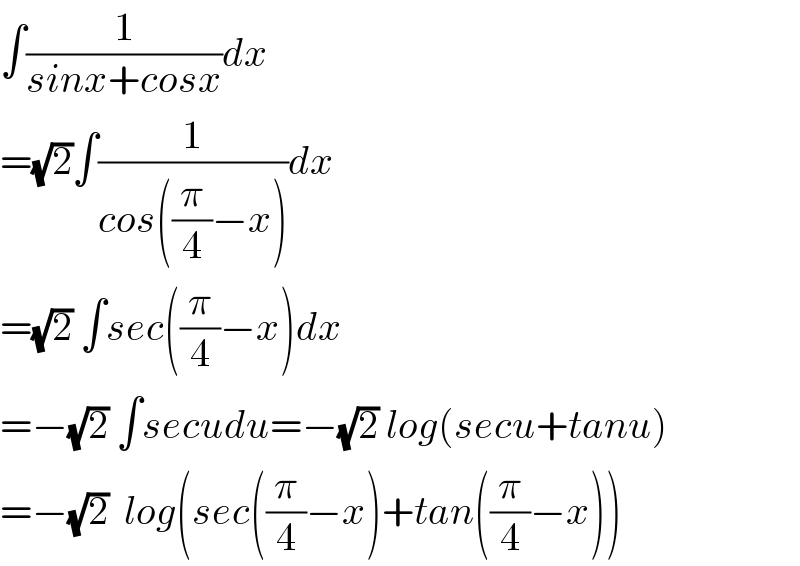
$$\int\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{sinx}+{cosx}}{dx} \\ $$$$=\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\int\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{cos}\left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}−{x}\right)}{dx} \\ $$$$=\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\:\int{sec}\left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}−{x}\right){dx} \\ $$$$=−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\:\int{secudu}=−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\:{log}\left({secu}+{tanu}\right) \\ $$$$=−\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\:\:{log}\left({sec}\left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}−{x}\right)+{tan}\left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}−{x}\right)\right) \\ $$
Commented by MJS_new last updated on 17/Sep/20

$$\mathrm{no}. \\ $$
