
Question Number 101891 by bobhans last updated on 05/Jul/20
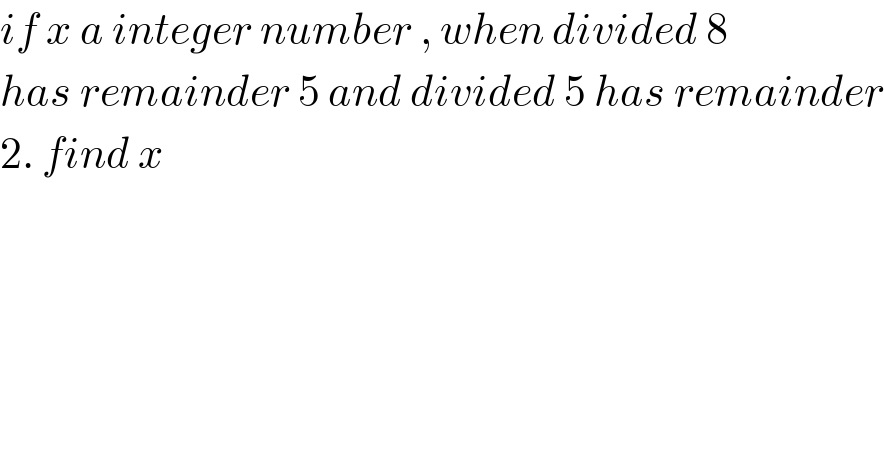
$${if}\:{x}\:{a}\:{integer}\:{number}\:,\:{when}\:{divided}\:\mathrm{8} \\ $$$${has}\:{remainder}\:\mathrm{5}\:{and}\:{divided}\:\mathrm{5}\:{has}\:{remainder} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}.\:{find}\:{x} \\ $$
Answered by Rasheed.Sindhi last updated on 05/Jul/20
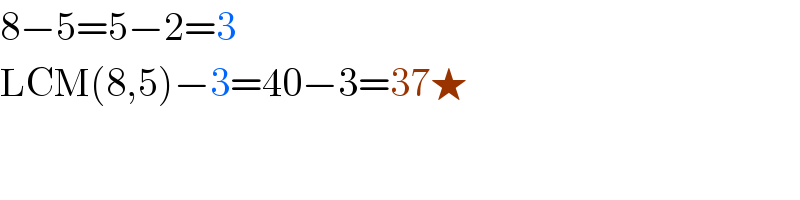
$$\mathrm{8}−\mathrm{5}=\mathrm{5}−\mathrm{2}=\mathrm{3} \\ $$$$\mathrm{LCM}\left(\mathrm{8},\mathrm{5}\right)−\mathrm{3}=\mathrm{40}−\mathrm{3}=\mathrm{37}\bigstar \\ $$
Commented by Rasheed.Sindhi last updated on 05/Jul/20
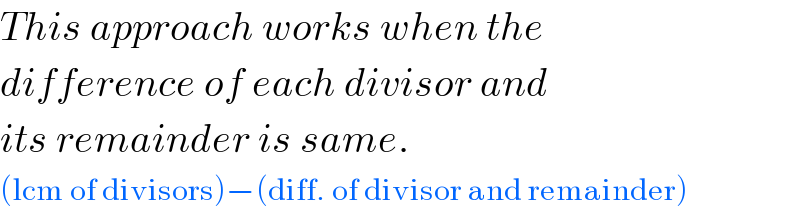
$${This}\:{approach}\:{works}\:{when}\:{the} \\ $$$${difference}\:{of}\:{each}\:{divisor}\:{and} \\ $$$${its}\:{remainder}\:{is}\:{same}. \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{lcm}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{divisors}\right)−\left(\mathrm{diff}.\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{divisor}\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{remainder}\right) \\ $$
Commented by bemath last updated on 06/Jul/20

$${great}\:{sir} \\ $$
Answered by john santu last updated on 05/Jul/20
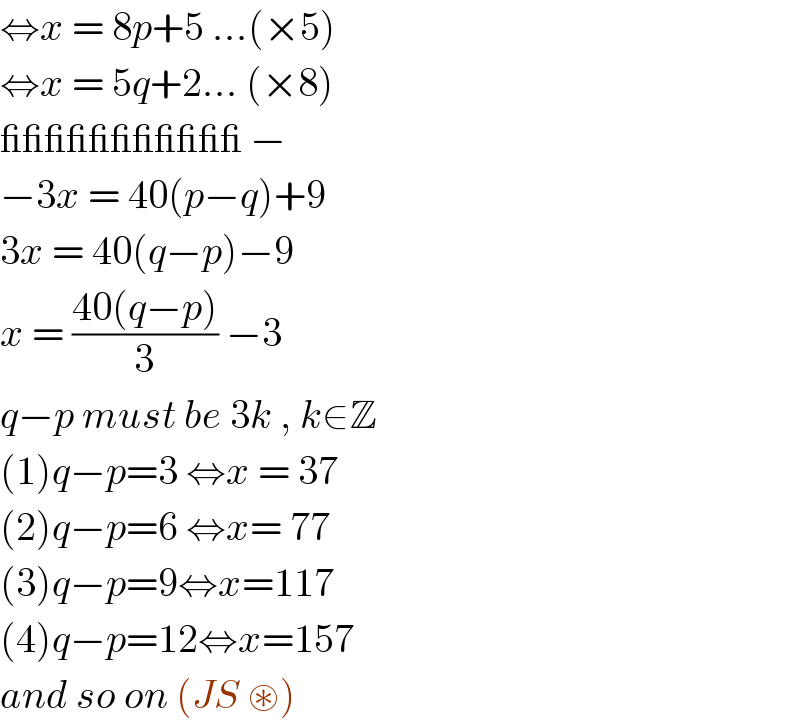
$$\Leftrightarrow{x}\:=\:\mathrm{8}{p}+\mathrm{5}\:...\left(×\mathrm{5}\right) \\ $$$$\Leftrightarrow{x}\:=\:\mathrm{5}{q}+\mathrm{2}...\:\left(×\mathrm{8}\right) \\ $$$$\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\:− \\ $$$$−\mathrm{3}{x}\:=\:\mathrm{40}\left({p}−{q}\right)+\mathrm{9} \\ $$$$\mathrm{3}{x}\:=\:\mathrm{40}\left({q}−{p}\right)−\mathrm{9} \\ $$$${x}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{40}\left({q}−{p}\right)}{\mathrm{3}}\:−\mathrm{3}\: \\ $$$${q}−{p}\:{must}\:{be}\:\mathrm{3}{k}\:,\:{k}\in\mathbb{Z} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{1}\right){q}−{p}=\mathrm{3}\:\Leftrightarrow{x}\:=\:\mathrm{37} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{2}\right){q}−{p}=\mathrm{6}\:\Leftrightarrow{x}=\:\mathrm{77} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{3}\right){q}−{p}=\mathrm{9}\Leftrightarrow{x}=\mathrm{117} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{4}\right){q}−{p}=\mathrm{12}\Leftrightarrow{x}=\mathrm{157} \\ $$$${and}\:{so}\:{on}\:\left({JS}\:\circledast\right)\: \\ $$
Answered by floor(10²Eta[1]) last updated on 22/Jul/20
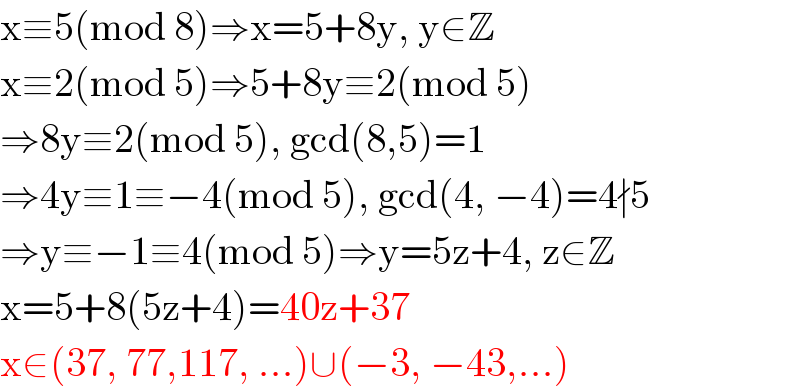
$$\mathrm{x}\equiv\mathrm{5}\left(\mathrm{mod}\:\mathrm{8}\right)\Rightarrow\mathrm{x}=\mathrm{5}+\mathrm{8y},\:\mathrm{y}\in\mathbb{Z} \\ $$$$\mathrm{x}\equiv\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{mod}\:\mathrm{5}\right)\Rightarrow\mathrm{5}+\mathrm{8y}\equiv\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{mod}\:\mathrm{5}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{8y}\equiv\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{mod}\:\mathrm{5}\right),\:\mathrm{gcd}\left(\mathrm{8},\mathrm{5}\right)=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{4y}\equiv\mathrm{1}\equiv−\mathrm{4}\left(\mathrm{mod}\:\mathrm{5}\right),\:\mathrm{gcd}\left(\mathrm{4},\:−\mathrm{4}\right)=\mathrm{4}\nmid\mathrm{5} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{y}\equiv−\mathrm{1}\equiv\mathrm{4}\left(\mathrm{mod}\:\mathrm{5}\right)\Rightarrow\mathrm{y}=\mathrm{5z}+\mathrm{4},\:\mathrm{z}\in\mathbb{Z} \\ $$$$\mathrm{x}=\mathrm{5}+\mathrm{8}\left(\mathrm{5z}+\mathrm{4}\right)=\mathrm{40z}+\mathrm{37} \\ $$$$\mathrm{x}\in\left(\mathrm{37},\:\mathrm{77},\mathrm{117},\:...\right)\cup\left(−\mathrm{3},\:−\mathrm{43},...\right) \\ $$
